MCAI Innovation Vision: The Commerce Clause as America’s AI Advantage
Constitutional Authority, National Innovation, and Global Foresight
I. Executive Summary: The Hidden Constitutional Key
The Constitution’s Commerce Clause (Art. I, Sec. 8, Cl. 3) has long been underestimated, treated as a mere allocation of power between states and Congress. In practice, it has been the decisive instrument for building national coherence in times of technological transformation. From the railroads to the Internet, the Clause has repeatedly allowed the federal government to impose uniform standards where fragmentation once reigned. Its importance today cannot be overstated: artificial intelligence, the defining infrastructure of the Intelligence Century, is inherently interstate and demands constitutional foresight.
AI does not stop at state borders. Data travels instantly across networks, training systems on inputs drawn from all corners of the country and globe. Compute resources are distributed across multiple states, power purchase agreements span decades, and AI-generated outputs shape national labor markets, securities trading, and healthcare delivery. In this context, the Commerce Clause is not an abstraction — it is the structural advantage that allows America to transform AI from a patchwork of local experiments into a unified national framework worthy of its scale.
MindCast AI’s Predictive Cognitive AI makes this foresight actionable. Our simulations use Cognitive Digital Twins to model state–federal conflicts, investor confidence cycles, and regulatory adoption curves, showing how the Clause translates into measurable advantages for innovation velocity and trust. In this way, the vision statement itself is powered by predictive foresight, not only historical analogy. Importantly, federal unity does not mean suppressing state creativity. As the vision develops, we emphasize how Commerce Clause leadership can absorb the most valuable state innovations, scaling them nationally while avoiding the inefficiencies of fragmentation.
Contact mcai@mindcast-ai.com to partner with us on AI policy.
II. Historical Lineage: Commerce as National Infrastructure
The United States repeatedly used the Commerce Clause to convert unruly innovation into trusted national systems. In the 19th century, interstate jurisdiction enabled Congress to tame railroad rate discrimination and standardize safety—turning disconnected lines into a continental network. In the early 20th century, aviation scaled only after federal standards unified airworthiness, air traffic, and liability, giving manufacturers and carriers a single rulebook. In the 1930s, securities laws restored confidence after the crash by imposing uniform disclosure and antifraud rules on offerings that routinely crossed state lines.
The Clause also powered moral transformation with economic logic. In the 1960s, Congress relied on the impact to interstate commerce to outlaw discrimination in public accommodations, recognizing that exclusion distorted national markets. The lesson across these chapters is consistent: federal coherence created trust; trust unlocked capital formation; capital formation scaled innovation. AI is the next such chapter—an infrastructure whose national integration will define growth and legitimacy for decades.
III. The Internet as a Commerce Clause Precedent
The Internet is the closest modern precedent because it was born interstate. Packets do not respect borders; e‑commerce, payments, and content distribution instantly crossed jurisdictions. Congress and federal regulators asserted primacy over core issues—online consumer protection, platform liability regimes, and digital transactions—so companies did not face fifty incompatible Internet codes. While particular statutes encountered constitutional limits, the system‑level result was clear: a national framework enabled scale.
That coherence produced an innovation flywheel. Startups could launch once and sell nationally; trust rules were predictable; capital concentrated into platforms that became global infrastructure. AI mirrors this posture: its data, compute, and outputs move across states by design. Treating AI like the Internet—interstate first—positions the U.S. to replicate that growth, while avoiding the patchwork that would throttle diffusion.
IV. AI as Interstate Commerce
Artificial intelligence implicates several distinct forms of commerce, and courts may evaluate each differently. First are data flows—training corpora and user data moving through cloud and edge networks—which raise privacy, attribution, and consumer‑protection issues tied to interstate services. Second are computational resources—chips, cloud capacity, colocation, and long‑term power contracts—concrete goods and services purchased and delivered across state lines. Third are AI outputs—generative content, risk scores, medical inferences—sold or deployed across markets in employment, finance, education, and health.
Acknowledging these categories clarifies doctrine while reinforcing reality: taken separately or together, the economic activity is inherently interstate. A federal framework can calibrate obligations per category (e.g., distinct audit and notice baselines for data inputs, safety/performance standards for compute‑bound systems, and transparency/remedy rules for outputs) while preserving a single national market for AI adoption.
V. Fragmentation vs. Unity
The dangers of fragmentation are already visible. California has advanced algorithmic accountability requirements that compel recurring impact assessments and disclosure for automated decision systems, with documentation formats that diverge from federal privacy templates. Illinois’s Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA) imposes strict informed consent and statutory damages for biometric capture, spawning extensive litigation and multimillion‑dollar settlements. Texas has proposed employment AI rules that require notice and post‑decision appeal windows when automated tools influence hiring, creating distinct procedural obligations.
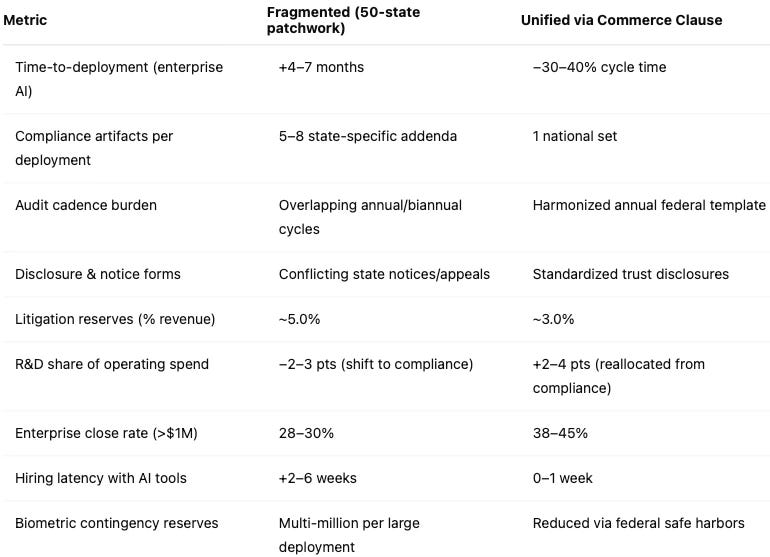
Together, these rules force duplicative audits and contradictory disclosures, and expose companies to venue‑specific liability theories. Compliance teams report that aligning a California audit cadence with Illinois consent workflows can add 4–6 months to enterprise contract cycles, while BIPA risk often requires multi‑million contingency reserves. Texas‑style appeal timelines extend hiring latency by 2–6 weeks, slowing adoption of AI‑assisted tools.
Foresight Cost Matrix (MindCast AI Predictive Cognitive AI — Cognitive Digital Twins)
Note: Directional scenario outputs from MindCast AI’s Predictive Cognitive AI; not legal or financial advice.
For a constitutional blueprint on unifying AI oversight, see MCAI Innovation Vision: The Federal Unification of Intelligence, AI Preemption and the Rise of National Foresight (June 2025).
VI. Innovation Advantage Through the Commerce Clause
Federal coherence does more than reduce paperwork—it produces innovation multipliers. Scale improves when founders ship to one national baseline rather than fifty. Trust increases when users encounter consistent protections and redress. Capital deepens as investors price lower regulatory uncertainty and faster enterprise sales cycles. These three effects—scale, trust, capital—compound into a durable national edge.
Centralization, however, carries risks. States serve as laboratories of democracy, discovering safeguards and pitfalls federal rules might miss. Commerce Clause leadership should therefore absorb and elevate proven state innovations rather than erase them. MindCast AI foresight scenarios compare two futures: (A) siloed state experiments that create uneven trust outcomes and compliance drag; (B) a unified framework that federates California audit tools and Illinois biometric safeguards into a single national standard—lowering variance while preserving inventive energy.
Related analyses: MCAI Innovation Vision: America Needs a National AI Revolution — A Vision for Pioneering the Future of Human‑AI Civilization (Aug 2025); MCAI National Innovation Vision: How the U.S. Can Foster AI Innovation Using Intellectual Property as a National Innovation System (Aug 2025).
VII. Global Duel: U.S. Chaos vs. China’s Coordination
America and China are competing innovation architectures. China’s disciplined coordination compresses decision cycles, aligns provincial specializations, and scales capital rapidly—but it risks rigidity when assumptions fail. America’s pluralism generates breakthrough variance, yet without unity it can dissipate in compliance drag and slow diffusion. Commerce Clause–driven unity supplies the missing discipline: it keeps the collisions that spark discovery while giving them one corridor to scale.
Predictive Cognitive AI scenarios:
Fragmented U.S.: 3–5 bespoke compliance addenda per state bloc; time‑to‑deployment slips +4–7 months; litigation reserves hover near 5% of revenue; R&D share falls 2–3 pts; federal procurement splinters.
Unified U.S.: harmonized audits, notices, and impact assessments; time‑to‑deployment improves 30–40%; litigation reserves trend toward 3%; R&D share rises 2–4 pts; enterprise close rates improve 10–15%; interoperability compacts export the U.S. standard.
This is disciplined chaos operationalized: pluralism continues to generate discovery, while federal unity serves as a scaling membrane. For the strategic context, see MCAI National Innovation Vision: The AI Duel of America’s Chaotic Advantage vs. China’s Disciplined Coordination (Aug 2025).
VIII. Constitutional Foresight: Commerce as Coherence
The Commerce Clause is America’s most adaptive constitutional instrument. It knit railroads into a network, aviation into an industry, securities into trusted markets, civil rights into enforceable guarantees, and the Internet into global infrastructure. Its power lies in recognizing when new forms of economic activity are functionally interstate and ensuring one coherent market.
MindCast AI’s Predictive Cognitive AI validates this role for AI governance. Our Cognitive Digital Twins model state–federal tensions, regulatory adoption curves, and institutional trust cycles, revealing how different applications of the Clause alter innovation velocity and resilience. Across scenarios, national coherence consistently produces faster corrective cycles, lower variance in trust outcomes, and stronger global competitiveness—turning legal doctrine into a living foresight engine.
Conclusion: Coherence and Experimentation Together
The future of AI governance will not be secured by uniformity alone, nor by uncoordinated state experiments. It will be secured by a constitutional architecture that balances coherence with adaptability. The Commerce Clause offers that balance: it unifies national markets while still allowing states to pioneer new protections, safeguards, and innovations that can later be scaled nationally.
MindCast AI’s foresight simulations demonstrate that this dual dynamic is the optimal path. When state innovations like California’s audit frameworks or Illinois’s biometric safeguards are federated into a single national system, compliance burdens fall, investor confidence rises, and America projects one trusted standard abroad. At the same time, the pluralism of American states continues to serve as a wellspring of innovation and experimentation.
History will remember whether the United States chose to wield the Commerce Clause narrowly as a legal mechanism or broadly as a foresight tool. By treating it as both, America can ensure AI governance that is nationally coherent, globally competitive, and locally adaptive. Coherence and experimentation are not rivals — together they are the formula for resilience in the Intelligence Century.