MCAI Culture Vision: The Signal Cycle- Restoring Cultural Innovation Through Cognitive Integrity
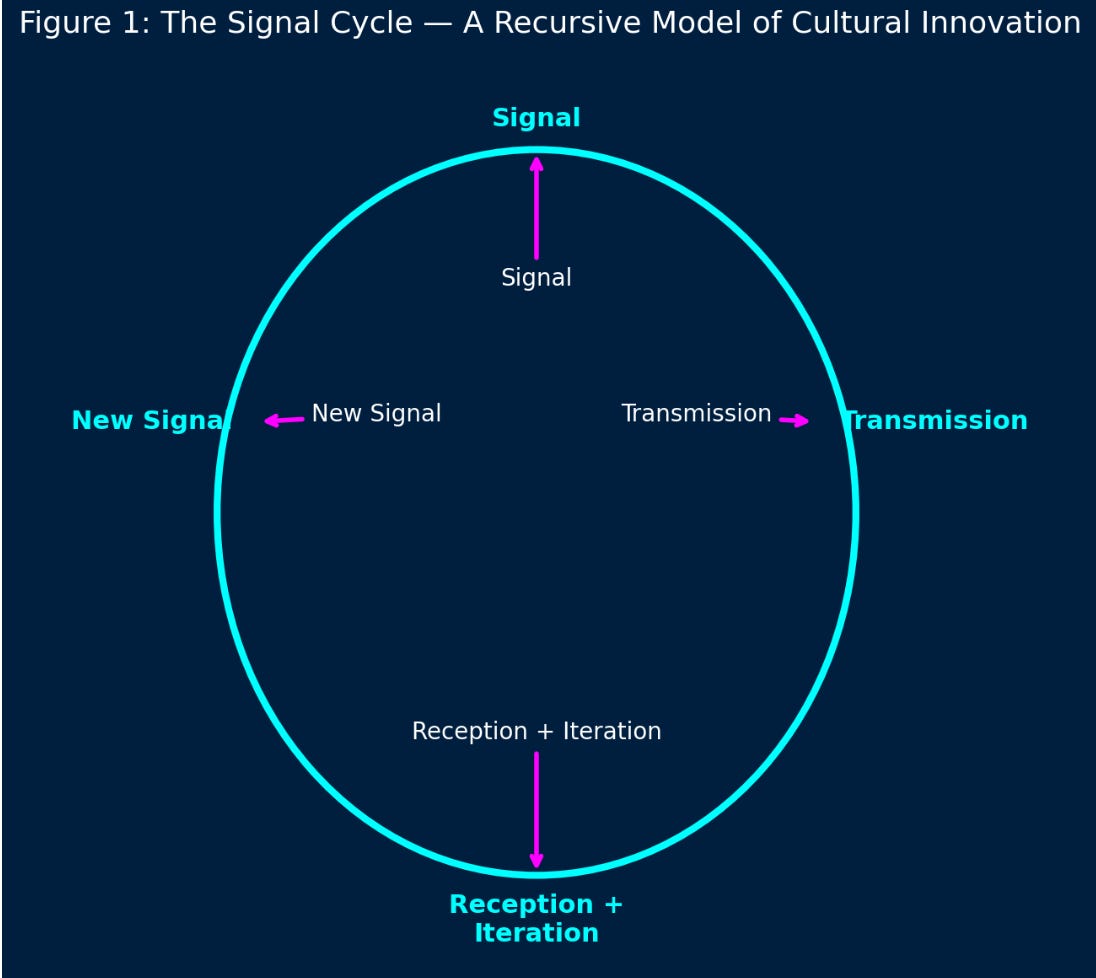
Cultural innovation = Signal → Transmission → Iterated Signal
Executive Summary
Cultural innovation depends on the recursive cycle between signal and transmission. Signal represents the emergence of original insight, value, or creative form. Transmission enables that signal to enter collective consciousness, where it can be interpreted, challenged, and iterated. Without transmission, signal remains isolated—brilliant but culturally inert. Without signal, transmission becomes noise—form without meaning, repetition without depth.
This white paper introduces the Signal Cycle framework: a model of cultural innovation as a recursive loop between signal, transmission, and iterated signal. It argues that cultural vitality arises not from one-time brilliance or mass amplification, but from systems that allow signal to be seeded, spread, received, and re-seeded.
Drawing from the works of Ralph Waldo Emerson (on originality and self-reliance), Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (on organic form), Friedrich Nietzsche (on recurrence and cultural degeneration), and William Shakespeare (on narrative recursion and tragic cycles), we explore how imbalance in the signal-transmission dynamic leads to cultural stagnation, shallowness, or isolation. We then show how Cognitive AI, particularly through the CulturalInnovationVision module, can detect where innovation loops have broken down—and forecast how they might be restored.
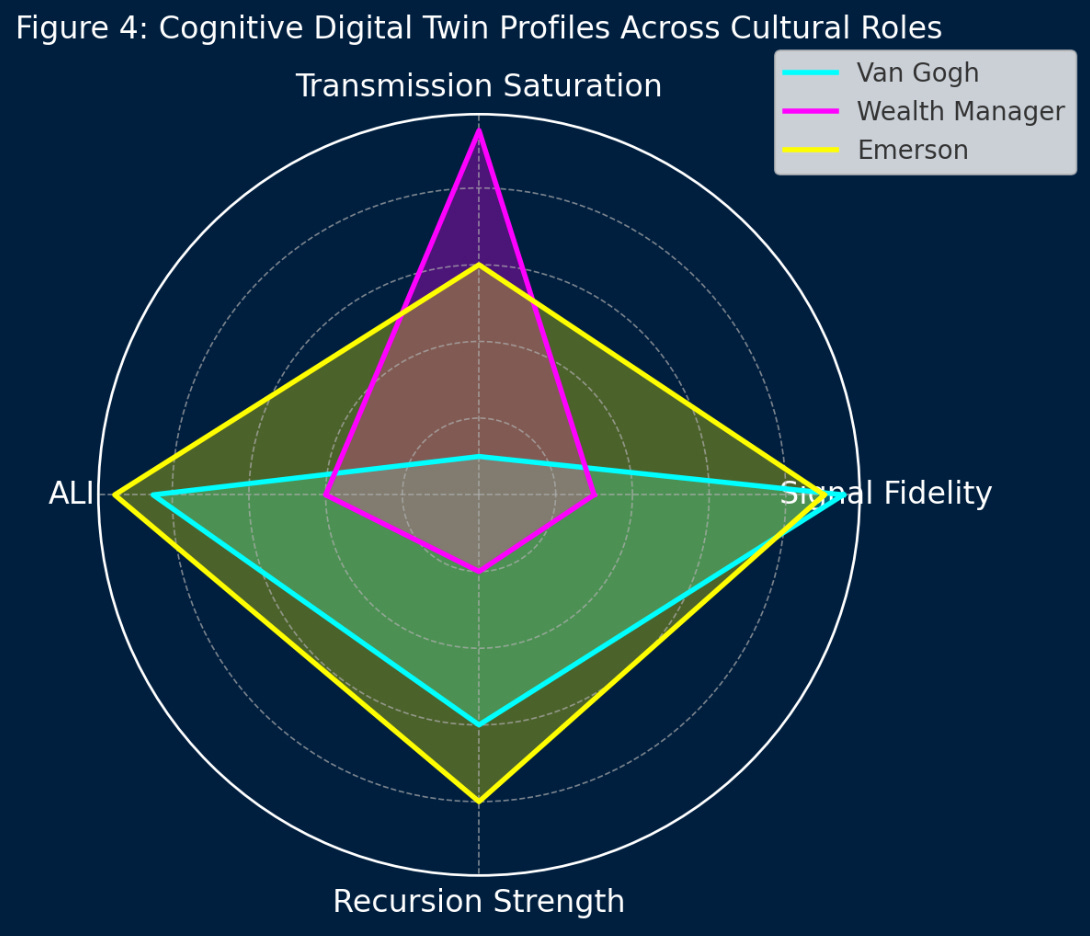
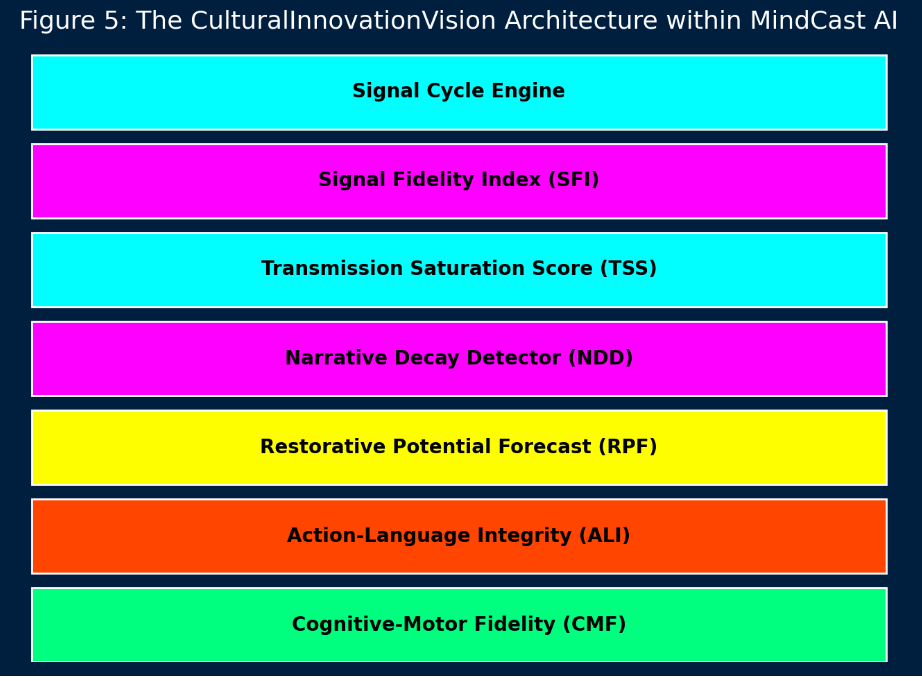
This white paper was produced by MindCast AI LLC (MCAI) using its proprietary Cognitive Digital Twin (CDT) technology, which simulates how individuals, institutions, and systems generate, transmit, and interpret meaning under varying cultural, narrative, and behavioral pressures. Through its specialized module—Cultural Innovation Vision—MCAI models the recursive cycle between signal and transmission, applies bias-aware forecasting tools, and evaluates cultural artifacts using metrics like Signal Fidelity Index (SFI), Transmission Saturation Score (TSS), and Action-Language Integrity (ALI).
MCAI’s simulation engine allowed us to reconstruct the cognitive posture of historical figures (e.g., Emerson, Goethe, Nietzsche, Shakespeare), archetypal professionals (e.g., artists, wealth managers, real estate brokers), and systemic behaviors (e.g., platform dynamics, meme culture) to diagnose cultural breakdowns and forecast conditions for innovation recovery. MindCast AI’s system is patent-pending and represents a new frontier in Cognitive Artificial Intelligence (CAI)—where culture is modeled not as content, but as decision structure and cognitive recursion.
I. The Signal Cycle: A New Framework for Cultural Innovation
Cultural innovation is not linear. It evolves through a recursive process: signal gives rise to transmission, transmission invites response and integration, and that in turn generates a new round of signal. The strength of a culture lies in how well it facilitates this full cycle—not just the creation of signal or the reach of transmission, but their feedback loop.
Signal—like an unspoken idea or unshared artwork—can exist in isolation. It may still carry value even if undiscovered. Transmission, however, is derivative by nature: it cannot exist without a source. In systems where transmission dominates, culture becomes mimetic, hollow, and repetitive. In systems where signal is preserved without dissemination, value is stranded.
When transmission becomes self-referential—optimizing for virality, shareability, or algorithmic trends—it forms a closed loop. These systems amplify what already circulates, regardless of its substance. The result is cultural atrophy: engagement metrics rise while innovation declines. Nietzsche’s warning about “the last men,” obsessed with comfort and imitation, echoes this phenomenon.
A seed without fertile ground withers. A field without seed grows nothing. Signal is the origin—the cognitive or emotional breakthrough. Transmission is the ecosystem—the social context that allows signal to take root. One without the other yields silence or noise. Goethe’s theory of organic form emphasizes that healthy growth is iterative and adaptive—not forced or synthetic.
Insight: Cultural health depends on recursive integration, not scale alone.
The metric for innovation is not volume of output, but the depth of the feedback loop. Are ideas being heard, reshaped, re-integrated? Are signals iterated upon, or merely echoed? True innovation sustains itself through recursive cycles—not just visibility.
II. Signal and Transmission: Definitions and Distortions
Signal originates from within. It reflects a shift in perception, a new emotional register, or a structural reordering of meaning. In Emerson’s terms, signal is the authentic voice—the inner genius not yet filtered by the crowd. It does not seek to be understood but to express what must be said. Signal is the anchor of cultural originality.
Transmission is the vehicle through which signal becomes legible to others. It includes performance, publishing, algorithmic reach, and social replication. Its role is not to replace signal but to give it form. When aligned with signal, transmission creates resonance. When misaligned, it dilutes or distorts.
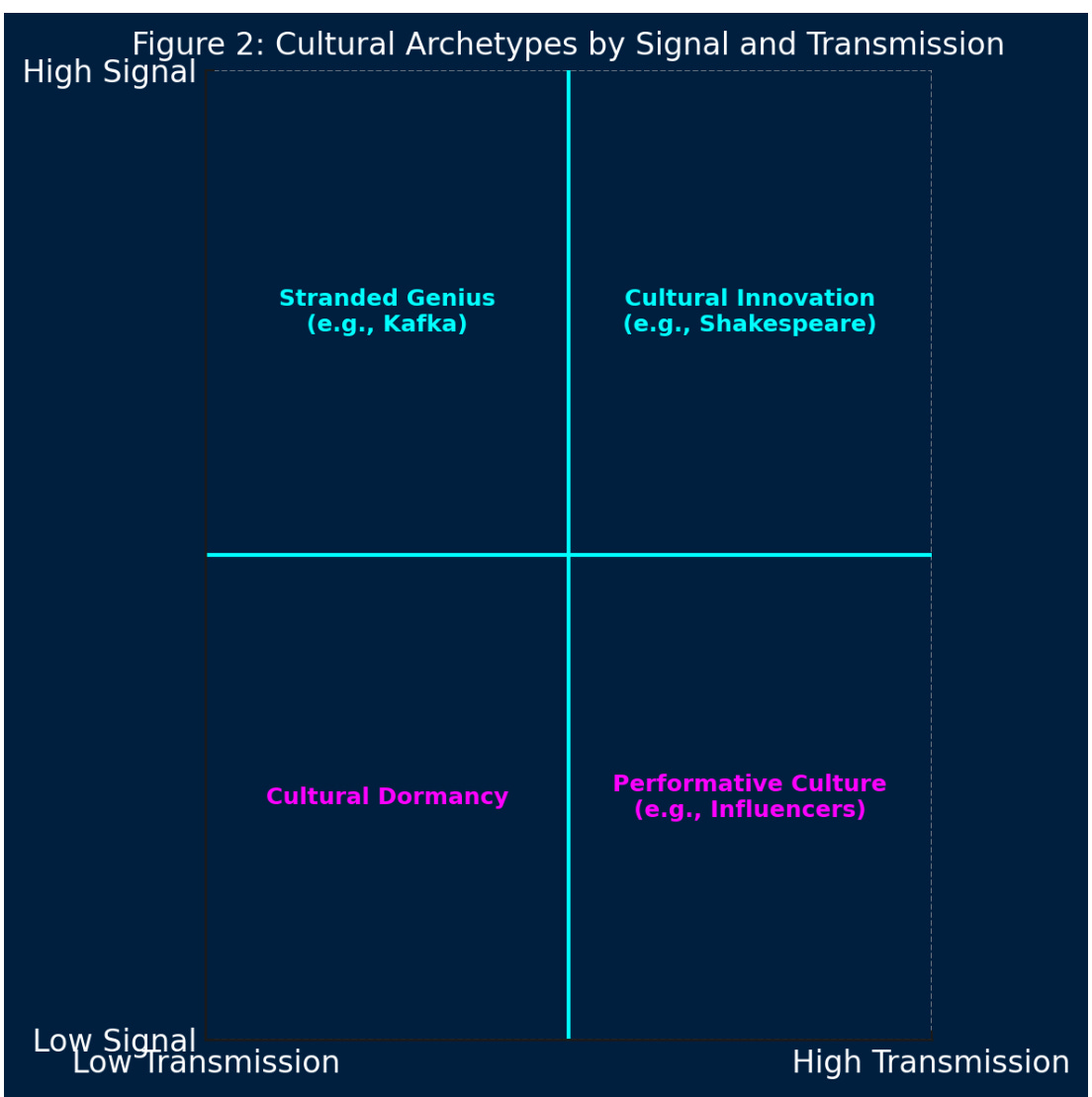
Some of the greatest minds have lived in obscurity. Kafka wrote for himself. Dickinson rarely published. Van Gogh sold only one painting in his lifetime. In these cases, the signal was strong—but the transmission system failed to catch it. Cultural ecosystems must be able to identify and integrate these unrecognized voices before their value is lost.
Modern content ecosystems often reward replication over innovation. High-transmission environments—especially digital platforms—prioritize attention metrics over substance. As a result, cultural products become optimized for engagement, not meaning. The outcome is repetition, burnout, and mistrust.
Emerson: On the Cost of Original Thought
Emerson believed that original thinkers must accept the price of misinterpretation. “To be great is to be misunderstood,” he wrote. This reveals a structural truth: signal often emerges ahead of its time, and early transmission may distort it. But the answer is not silence—it is alignment, where signal meets transmission with integrity.
Insight: Transmission that outruns signal becomes cultural extraction.
When transmission is no longer rooted in signal, it becomes extractive: using culture for gain without contribution. Institutions, platforms, and creators must be vigilant—transmission is not neutral. It either amplifies integrity or accelerates decay.
III. When There Is Only Signal: The Isolation of Genius
Not all signal becomes culture. History reminds us that innovation, no matter how brilliant, does not guarantee integration. When signal is not met with transmission—when the insight remains unseen, unread, or unshared—it becomes a private archive rather than a public transformation. Genius, in these cases, lives and dies in silence. Innovation without transmission is not failure, but it is isolation.
The most original ideas often emerge far beyond the horizon of what society is ready to hear. This does not mean they lack value—it means the world has no conceptual slot to receive them. These signals are outliers in their time, misunderstood not because they are wrong, but because they are premature. The cultural frontier begins with silence, and those who innovate without transmission live at its edge.
Emerson’s “Aboriginal Self” and the Inner Voice
Ralph Waldo Emerson understood this dynamic well. He wrote of the “aboriginal self”—a source of intuitive originality that cannot be sourced from imitation. Emerson urged thinkers to trust their voice even if misunderstood. But that voice, when left untranslated or untransmitted, becomes a solitary echo. Self-reliance is noble, but culture requires bridges from the self to society.
Case Insight: Van Gogh, Dickinson, Kafka
Vincent van Gogh died thinking he was a failure. Emily Dickinson published only a handful of poems in her lifetime. Franz Kafka instructed that his unpublished manuscripts be burned after his death. These were not just misunderstood artists—they were high-signal individuals with no transmission loop. Only after their deaths did the world develop enough interpretive capacity to integrate their signal. Their value was not diminished—it was simply deferred.
Insight: Innovation without reception is exile; we must rescue stranded signal.
Cultural systems must recognize that not all signal is immediately legible. Part of cultural stewardship is the active search for signal stranded by time, context, or convention. We must develop interpretive institutions capable of rescuing genius before it disappears.
IV. When There Is Only Transmission: The Collapse Into Cultural Echo
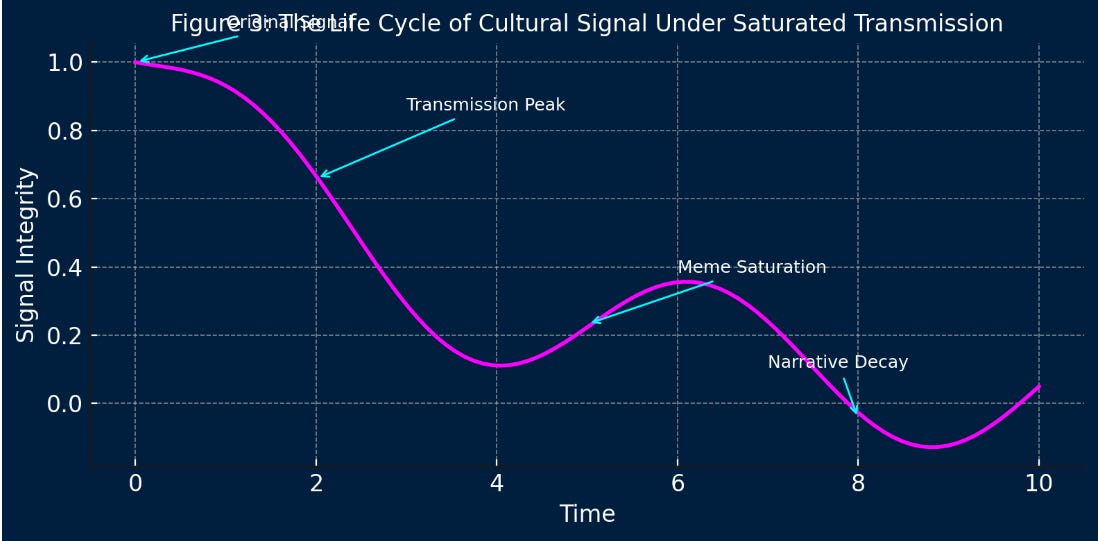
Over transmission can lead to the decay of meaning through mimetic loops. Transmission without signal is not culture—it is noise. When systems prioritize reach over originality, what emerges is an endless cycle of mimicry. The same structures, slogans, and aesthetics repeat with slight variation, not because they carry new meaning, but because they are optimized for attention. Transmission becomes self-referential. Meaning fades.
Nietzsche on Herd Thought and the Spectacle
Nietzsche warned of herd morality—the instinct to conform rather than think. In high-transmission environments, herd logic becomes spectacle. Visibility becomes the new virtue. Originality is sacrificed for shareability. The thinker is replaced by the influencer. The poet by the content strategist. Signal becomes vestigial, a liability in systems designed to maximize engagement.
From Meme to Void: Algorithmic Saturation
On platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube, the algorithm rewards replication. Virality becomes the standard of value. The result is cultural entropy. Memes that once carried subversive insight become hollow shells. Sounds, aesthetics, and gestures are recycled until their origin is forgotten. The loop closes. Nothing new enters.
Shakespeare’s Fool and the Hollow Court
Shakespeare often used fools to deliver truth to power. But in cultures of pure transmission, the court is ruled by the fool—and no one recognizes the inversion. Applause becomes the only currency. The crowd’s approval replaces the critic’s eye. The fool no longer subverts; the fool leads.
In some high-status professional spaces, transmission is often mistaken for value. A polished LinkedIn post, a sleek video tour, or a buzzword-heavy presentation creates the illusion of expertise. But when the underlying insight is shallow—when there is no cognitive differentiation behind the performance—these professionals become vessels of transmission only. They speak fluently, but say nothing. They accumulate clients, but not depth.
Insight: Visibility without signal creates reputational debt and cultural fatigue
Systems that reward pure transmission eventually cannibalize themselves. They elevate those who perform best, not those who think best. This leads to fatigue—not just for the audience, but for the culture itself. Institutions must re-anchor value in cognitive signal, not in volume of visibility.
V. The Five Theses of the Signal Cycle
Cultural innovation is not accidental—it follows identifiable patterns of emergence, dissemination, and recursion. When signal and transmission are in balance, new ideas are introduced, socially integrated, and iteratively evolved. When they are not, culture either stagnates in obscurity or collapses into spectacle. To understand how cultural systems sustain or fail innovation, we introduce five core theses.
1. The Paradox of Visibility
For innovation to thrive, it must be seen. But too much visibility, too early, can distort signal. Culture needs transmission, but the wrong kind suffocates originality. The paradox is that the very thing that sustains signal can also destroy it.
2. Signal is the Seed, Transmission is the Soil
Signal initiates. Transmission integrates. Signal alone cannot grow. Transmission alone cannot create. When balanced, the two form the basis of a living culture. When separated, one dies in silence, the other decays in noise.
3. The Mismatch Explains Shallow Trends
When transmission outweighs signal in cultural ecosystems, shallow trends dominate. These trends rise quickly but leave no residue. They feel urgent but not enduring. The mismatch explains why innovation feels scarce even in hyper-productive systems.
4. Cognitive AI as a Restorative Filter
Cognitive Artificial Intelligence can detect the asymmetry. It can model whether an agent or artifact contains original thought or mimics high-transmission norms. Through tools like Action-Language Integrity (ALI) and Narrative Recursion Modeling, AI can identify where signal has been lost—and where it might be revived.
5. Signal-Transmission-Feedback as Cultural Evolution
Cultural health is not measured in output, but in recursion. Signal must travel, return, and evolve. That is the cycle of innovation. The cultures that sustain this loop flourish. The cultures that break it—either through isolation or saturation—decline.
Each thesis captures a structural truth about how signal and transmission interact—why visibility can become distortion, why originality needs soil to grow, why shallow trends thrive in high-transmission systems, and how Cognitive AI can now diagnose and repair these fractures. Together, these five theses offer a framework—a recursive diagnostic—for evaluating the health of any cultural ecosystem.
Goethe: On Natural Growth and Form
Goethe believed in morphological evolution—form emerging through iterative adaptation. Culture, he argued, must grow organically. It cannot be engineered through brute force transmission. It must respond to the soil of its time, the signal of its age.
Nietzsche: On the Rebirth of Value
For Nietzsche, innovation was not linear progress, but eternal return—rebirth of value through re-engagement with origins. The Signal Cycle echoes this insight: new signal must emerge from the exhausted loops of transmission. That is the only path forward.
Insight: These theses form a recursive diagnostic for cultural ecosystems.
Together, these theses provide a framework for evaluating where culture stands in the cycle—what phase it’s in, where it’s breaking, and how it might be repaired.
Prepared by Noel Le, Founder | Architect of MindCast AI LLC. Noel holds a background in law and economics, and behavioral economics. He spent his career developing advanced technologies for intellectual property management.
LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/noelleesq
Email: mindcast.ai@icloud.com