MCAI Economics Vision: Chicago School Accelerated — Integrated Application, the NCAA NIL Interregnum
NIL Governance After Congressional Gridlock
Executive Summary
Congress has stalled. The SCORE Act collapsed in committee, the SAFE Act lacks momentum, CARA faces an uphill path, and HUSTLE addresses only fragments of the system. Meanwhile, the $2.8 billion settlement with the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA)—House v. NCAA—is now operational. Revenue-sharing caps, College Sports Commission (CSC) registration, Name, Image, and Likeness (NIL) GO approval protocols, and Deloitte clearinghouse functions are live. Congress has effectively delegated governance to a settlement infrastructure it did not design and cannot modify.
The result is what MindCast AI terms the Interregnum—a period where no single authority commands legitimacy, multiple actors compete to define rules, and structural strain accumulates without release. The interregnum is not chaos. It is a temporary governance regime under load, with identifiable stress nodes and predictable failure modes. Among those failure modes is a risk particular to academic-first institutions: lag-convergence hypocrisy, where delayed adoption of market practices creates greater exposure than early adoption would have.
Chicago School Accelerated: The Analytical Frame
The interregnum is a Chicago School problem in a modern operating environment. Coase explains why coordination collapses when focal points and trust density degrade even if information and contracting tools exist. Becker explains why rational actors exploit the resulting ambiguity by optimizing around enforcement and routing value through intermediaries. Posner explains why courts and regulators struggle to correct in time because fragmented governance converts the learning environment from “kind” to “wicked.” The result is a settlement-built regime that functions as infrastructure but lacks sovereign legitimacy, making legitimacy shocks—not gradual convergence—the dominant path to reset.
The publication applies the Chicago School Accelerated framework, which modernizes the Chicago School of Law and Economics through behavioral economics. MindCast AI’s Cognitive Digital Twin (CDT) methodology, simulated through our Vision Functions, operationalizes the Coase→Becker→Posner sequence as measurement interfaces rather than theoretical abstractions. The framework treats coordination capacity (Coase), incentive exploitation (Becker), and institutional correction lag (Posner) as state variables that evolve over time and interact to produce the governance dynamics observed in the interregnum.
Key Predictions
The simulation generates five forward scenarios with probabilistic weightings over a twelve-to-thirty-six-month horizon:
Patchwork persistence (38%): Coordination fragmentation continues without a single forcing shock. The market stratifies by compliance sophistication. Sophisticated intermediaries win; mid-majors and low-documentation actors lose.
Legitimacy collapse (24%): Selective enforcement combined with high-profile leaks destroys compliance incentives. Rational actors openly defect. Plaintiffs and political entrepreneurs win; settlement enforcement credibility collapses.
Employee classification cascade (18%): Courts rule that control-plus-pay facts constitute employment. Retroactive liability follows years of interim practices. Athlete bargaining power increases; informal pay structures face exposure.
Conditional federal re-entry (16%): A public failure event forces Congress to return with legislation featuring audits, mandatory disclosure, and bounded antitrust immunity. Institutions that prepared auditability survive; late adopters do not.
Durable settlement governance (4%): Enforcement legitimacy improves enough that the settlement infrastructure stabilizes without federal intervention. Compliance leaders win; arbitrage models compress.
The interregnum will end through a legitimacy break, not through quiet convergence. A trigger event—selective enforcement, a major leak, or an employment classification shock—will force either court-built labor rules or conditional federal intervention.
Prior MindCast AI Work on College Athletics Name, Image, and Likeness
The simulation builds on an extensive body of MindCast AI analysis developed between May and September 2025. That work traced the dismantling of amateurism through litigation, modeled institutional risk under the House v. NCAAsettlement, evaluated competing congressional proposals, and simulated how federal enforcement posture affects university governance strategies.
Key prior publications include the National Name-Image-Likeness Simulation Framework (July 2025), which evaluated seven nationally prominent institutions across a tiered risk matrix and introduced the Cognitive Digital Twin methodology for NIL governance analysis. The Foresight Simulation of the SCORE Act and NCAA Settlement (July 2025) stress-tested proposed legislation and identified structural brittleness in static compliance frameworks. Analysis of Department of Justice (DOJ) Participation in Zeigler v. NCAA (June 2025) revealed a federal shift toward institutional deference that reshaped university risk calculations. The SAFE vs. SCORE Act Comparison (September 2025) mapped the congressional stalemate and introduced conditional safe harbor as a legislative design principle. The University of Washington NIL Compliance Matrix (July 2025) demonstrated how foresight simulation applies to specific institutional contexts.
Those simulations asked what Congress might do and modeled pre-settlement uncertainty. This simulation asks a different question: what happens because Congress failed to act? The interregnum treats the House settlement as infrastructure, not resolution, and centers legitimacy and enforcement capacity rather than legislative ideology. Full citations appear in the Sources Appendix.
Document Roadmap
Section I establishes why the interregnum requires a new simulation distinct from prior work.
Section II maps the NIL governance system as four interacting vectors, each with Chicago School mappings identifying coordination questions (Coase), exploitation dynamics (Becker), and correction constraints (Posner).
Section III explains the Coase→Becker→Posner sequence as a foresight engine, operationalized through Cognitive Digital Twin methodology simulated via eight Vision Functions.
Section IV presents quantitative results and narrative interpretation for each Vision Function, with falsification contracts specifying conditions that would require revision.
Section V translates simulation outputs into predictions about institutional behavior, differentiating by institutional type.
Section VI provides tailored guidance for university presidents, athletic directors, general counsels, lawmakers, and high-potential athletes.
Section VII distills the simulation findings into consolidated takeaways.
Sections VIII–IX collect falsification contracts and source citations.
Contact mcai@mindcast-ai.com to partner with us on NCAA NIL foresight simulations and compliance.
I. The Governing Problem
The NIL governance environment has entered a phase distinct from anything previously modeled: congressional failure combined with operational settlement infrastructure and visible market adaptation. The combination requires its own foresight architecture.
Why the Interregnum Requires a New Simulation
Three conditions changed simultaneously. First, Congress has stalled—no near-term federal coherence is available. Second, the House settlement has operationalized—caps, enforcement bodies, and reporting thresholds are live. Third, market adaptation is already visible—schools, collectives, brands, and private capital are restructuring around enforcement risk.
That combination creates a stable-but-fragile interim equilibrium. Universities cannot wait for legislation that may not arrive. Enforcement bodies must act without statutory authority. Athletes must navigate a system where the rules are contested and the enforcers lack legitimacy. The situation presents a classic foresight trigger: a temporary governance regime under strain, where legitimacy, coordination capacity, and adaptive learning determine stability more than statutory text.
The interregnum will not resolve through quiet convergence. It will end through a legitimacy break—selective enforcement, a major leak, or an employment classification shock—that forces either court-built labor rules or conditional federal intervention. Understanding how the system behaves in the interim is essential for every actor within it.
The interregnum is neither chaos nor stability. It is a contested governance period where the absence of federal legitimacy forces institutions, enforcement bodies, and market actors to improvise. The simulation maps how that improvisation unfolds.
II. The Foresight Architecture
The NIL governance system operates as four interacting vectors, each with distinct incentives, constraints, and failure modes. The following analysis maps those vectors and establishes the Chicago School questions that structure the analysis of each.
A Framework for Distributed Governance Analysis
The vectors are:
(1) the Institutional Core, comprising universities and conferences that implement NIL policy;
(2) the Enforcement and Legitimacy Layer, comprising the College Sports Commission, NCAA enforcement functions, and state attorneys general;
(3) Market Actors, comprising athletes, collectives, brands, and private capital that move money through the system; and
(4) the Federal and Judicial Horizon, comprising courts, agencies, and Congress as potential corrective forces.
Each vector can fail independently, but failures cascade across vectors in predictable ways.
Vector 1: Institutional Core
The Institutional Core comprises the universities and conferences that must operationalize NIL governance without clear federal guidance. The vector includes Power Two conferences (Big Ten, Southeastern Conference), representative high-revenue universities, academic-first governance clusters (Ivy-style institutions), and mid-major programs operating with fewer resources and less enforcement attention. Academic-first institutions face a distinctive risk that will recur throughout this analysis: lag-convergence hypocrisy, where delayed adoption of market-mimicking practices creates reputational and legal exposure greater than early adoption would have.
Chicago mapping: Coase asks whether institutions can coordinate on a stable internal rule set without a sovereign focal point. Becker asks which schools optimize by boundary-testing through Limited Liability Companies (LLCs), deliverables, and routing. Posner asks which governance designs survive discovery and survive the lag between conduct and correction.
The core question for this vector is whether institutions can internalize NIL post-settlement in ways that are legally defensible, narratively coherent, and competitively sustainable. Key variables include governance centralization, above-cap revenue strategies, Title IX exposure tolerance, and willingness to sign CSC participation agreements. Failure modes include shadow compensation triggering attorney general scrutiny, Title IX distribution challenges, and evidence of collusive peer-mirroring.
Vector 2: Enforcement and Legitimacy Layer
The Enforcement and Legitimacy Layer comprises the bodies responsible for monitoring and enforcing NIL rules without statutory backing. The vector includes the College Sports Commission (the settlement’s designated enforcement body), NCAA enforcement functions (operating with diminished credibility), and coalitions of state attorneys general acting as fragmented enforcers with political incentives. The CSC’s core legitimacy deficit reduces to a simple formulation: its authority is contractual rather than sovereign, procedural rather than democratic, and enforceable only so long as powerful members continue to consent.
Chicago mapping: Coase asks whether the CSC is a credible focal point for coordination. Becker asks whether actors arbitrage selective enforcement. Posner asks whether fragmented enforcement creates doctrinal and feedback lag that makes correction late.
The core question for this vector is whether the CSC can function as a legitimate quasi-regulator without congressional authorization. Key variables include NIL GO approval consistency, state transparency laws (Oregon, New Jersey), scope of CSC authority under membership agreements, and attorney general coalition behavior. Failure modes include patchwork enforcement, selective non-compliance by powerful programs, and court challenges to CSC authority.
Vector 3: Market Actors
Market Actors comprise the entities that move money through the NIL system and respond to incentive structures set by institutions and enforcement bodies. The vector includes the athlete representation ecosystem (agents, advisors), collectives (booster-linked and hybrid structures), brands (risk-managed sponsors), and private capital (risk-sensitive investors evaluating the space).
Chicago mapping: Coase asks whether markets share “valid business purpose” as a genuine focal point or treat it as theater. Becker asks who captures value—athletes versus intermediaries—under cap constraints. Posner asks when harms become legally legible through documentation failures or misclassification rulings.
The core question for this vector is how money flows when “valid business purpose” gates access and enforcement remains inconsistent. Key variables include the shift from booster cash to brand-safe deals, private equity tolerance for governance risk, athlete bargaining power under cap constraints, and documentation sophistication. Failure modes include systematic underpayment triggering antitrust suits, overpayment triggering employment classification, and capital flight from high-risk programs.
Vector 4: Federal and Judicial Horizon
The Federal and Judicial Horizon comprises the actors capable of providing authoritative resolution but currently absent from active governance. The vector includes federal courts (as institutional correction mechanisms), federal agencies with labor and competition relevance (Federal Trade Commission (FTC), Department of Labor (DOL), National Labor Relations Board (NLRB), Internal Revenue Service (IRS)), and Congress (as a learning and coalition system with low adaptive velocity).
Chicago mapping: Coase observes that Congress failed to supply a focal point, so fragmentation persists. Becker observes that political actors optimize on blame assignment after shocks rather than prevention before them. Posner observes that the correction window opens only after a salient trigger event—the wicked learning environment ensures law arrives late.
The core question for this vector is which pressures eventually compel federal action—and on what timeline. Key variables include the Johnson v. NCAA trajectory, Title IX appellate dynamics, agency signaling, and political realignment around women’s sports and state attorneys general. Failure modes include forced employee classification, federal intervention after market breakdown, and retroactive liability from interim practices.
The 4 prong vector architecture reveals that NIL governance is not a single policy problem but a distributed coordination challenge. Each vector can fail independently, but failures cascade across vectors in predictable ways. The methodology that follows provides the analytical engine for tracing those cascades.
III. Chicago Accelerated Method: Coase→Becker→Posner as a Foresight Engine
With the foresight architecture established, this section explains how the Chicago School Accelerated framework becomes an analytical engine. MindCast AI’s CDT methodology models how institutional actors behave under specific conditions, generating quantitative metrics and predictive outputs. Eight Vision Functions simulate the CDTs, operationalizing the Coase→Becker→Posner sequence as measurement interfaces: coordination capacity, incentive exploitation, and institutional correction lag become state variables that evolve over time.
The Causal Logic of the Simulation
The interregnum is a legitimacy and coordination problem under strain, not a pricing or ideology problem. The CDT methodology must therefore diagnose coordination capacity, model exploitation once coordination weakens, test institutional correction capacity, and stress legitimacy under enforcement ambiguity.
The sequence runs: Coase Vision (can the system still coordinate?) → Becker Vision (who exploits when it cannot?) → Integrity Vision (do institutions hold under stress?) → Regulatory Vision (does enforcement consolidate or fragment?) → Disclosure Vision (where does secrecy backfire?) → Institutional Cognitive Plasticity Vision (can institutions adapt?) → Posner Vision (can law correct in time?) → Integrated Foresight Vision (how does the interregnum end?). Each stage has defined parties, outputs, and threshold signals that trigger the next stage.
The Eight MindCast AI Vision Functions
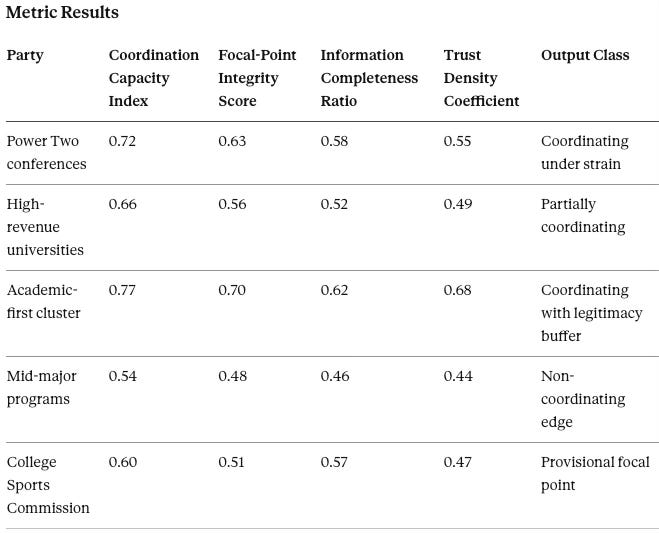
Coase Vision diagnoses whether NIL coordination is still possible without Congress. It runs on the NCAA, College Sports Commission, Power Two conferences, and academic-first governance clusters. Key outputs include Coordination Capacity Index, Focal-Point Integrity Score, and Trust Density Coefficient. If coordination capacity falls below threshold, downstream exploitation becomes rational rather than deviant.
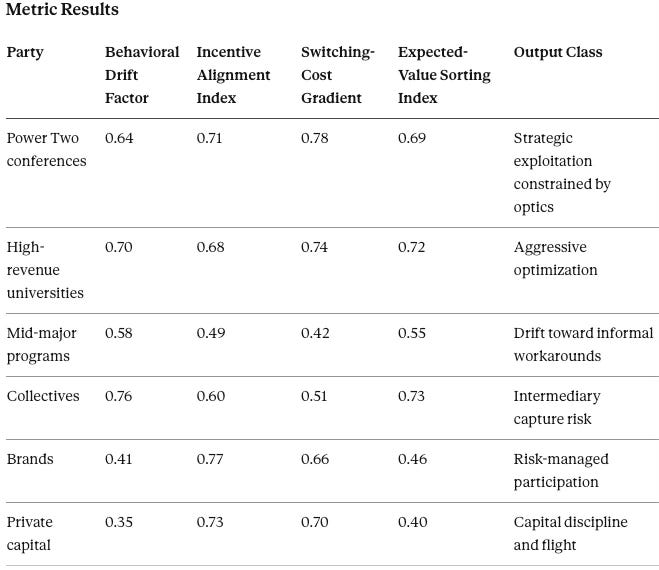
Becker Vision models how rational actors exploit the system once coordination weakens. It runs on Power Two conferences, high-revenue universities, collectives, and brand/agency intermediaries. Key outputs include Behavioral Drift Factor, Incentive Alignment Index, and Expected-Value Sorting. If exploitation becomes the dominant strategy, enforcement legitimacy faces stress-testing.
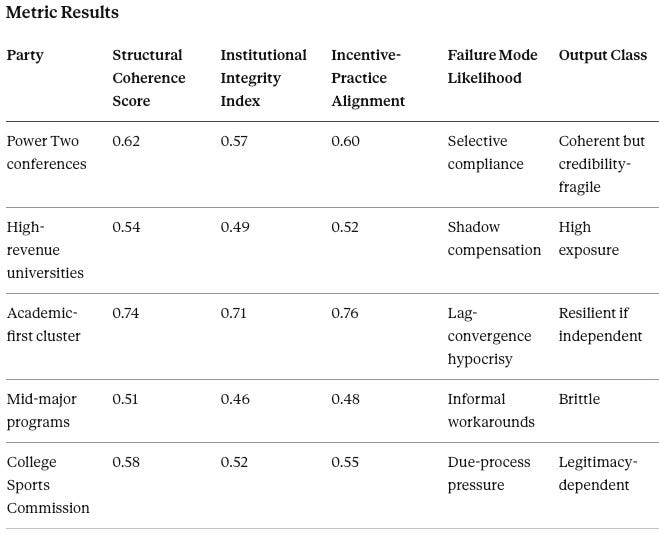
Integrity Vision evaluates whether institutions maintain structural coherence under pressure. It runs on universities by cluster (Power Two, mid-major, academic-first), conference offices, and the CSC. Key outputs include Structural Coherence Score, Institutional Integrity Index, and Failure Mode Classification. Low integrity combined with high exploitation signals legitimacy collapse risk.
Regulatory Vision models enforcement behavior in a fragmented authority environment. It runs on the CSC, state attorneys general coalitions, and NCAA enforcement. Key outputs include Enforcement Throughput, Jurisdictional Fragmentation Index, and Selective Enforcement Probability. If enforcement fragments, the federal and judicial horizon activates.
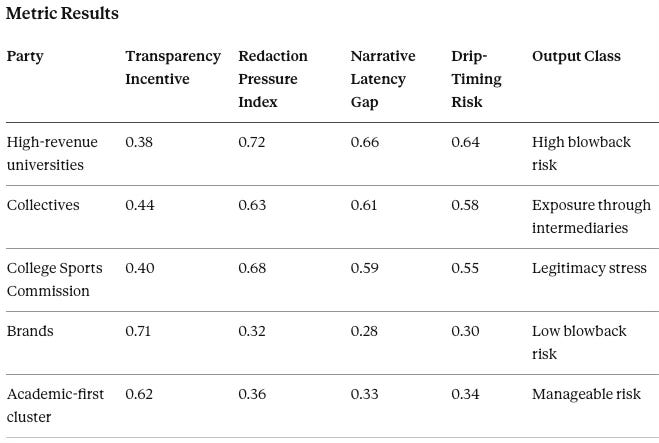
Disclosure Vision predicts transparency failures and narrative blowback. It runs on universities with complex NIL structures, the CSC, and high-visibility collectives. Key outputs include Narrative Latency Gap, Redaction Pressure Index, and Transparency Failure Probability.
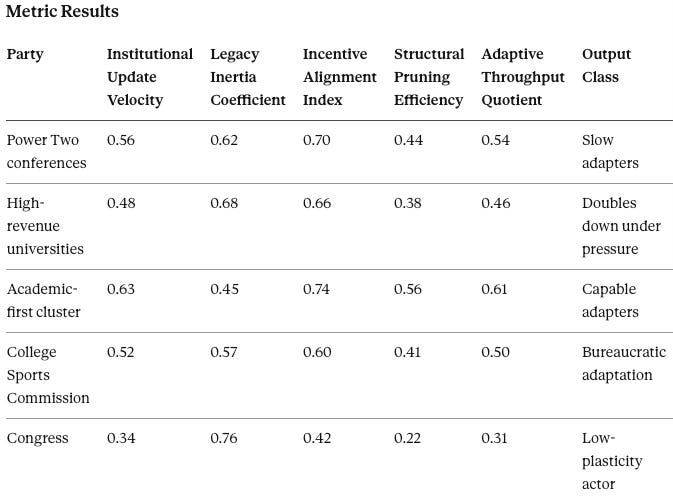
Institutional Cognitive Plasticity (ICP) Vision assesses whether institutions can adapt or only double down. It runs on the NCAA, CSC, Power Two conferences, and academic-first institutions. Key outputs include Institutional Update Velocity, Legacy Inertia Coefficient, and Adaptive Throughput Quotient. Low plasticity predicts institutional self-destruction under prolonged vacuum.
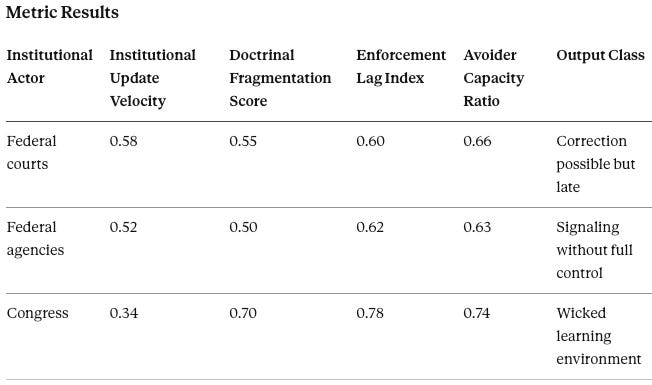
Posner Vision evaluates whether legal correction can occur before systemic harm locks in. It runs on federal courts, Congress, and relevant federal agencies. Key outputs include Enforcement Lag Index, Doctrinal Fragmentation Score, and Correction Feasibility Window.
Networked Outcome Evaluation Logic (MCAI) Foresight Vision integrates all vectors into forward scenarios. It runs on the entire NIL system as a composite CDT, producing time-to-regime-shift estimates, dominant end-state classifications, and early-warning indicators by vector.
The eight-stage Vision Function simulation mirrors the real-world causal sequence: coordination failure → exploitation → integrity strain → enforcement stress → narrative exposure → adaptation failure or success → legal correction → regime shift. The section that follows presents the quantitative results of running this engine on the NIL governance system.
IV. Vision Function Analysis: Results by Stage
The following analysis presents the quantitative outputs of each Vision Function CDT simulation, along with narrative interpretation and predictive conclusions. Each stage builds on the findings of the previous stage, creating a cumulative picture of system behavior. The falsification contracts at the end of each stage specify conditions that would require revision of the analysis.
IV.A. Coase Vision: Coordination Capacity Assessment
Chicago diagnosis: Coordination capacity is the missing variable.
The first diagnostic question is whether the NIL system can still coordinate on a stable rule set without Congress. Coordination does not require agreement on ideology or fairness. It requires that actors can identify focal points, maintain trust across repeated interactions, and reduce transaction costs through shared expectations. The Coase Vision CDT simulation tests whether these conditions hold.
Interpretation
Coordination holds in the Power Two because money, media schedules, and competitive symmetry force repeated games. Trust remains thin because schools fear selective enforcement and competitor arbitrage. The conferences can coordinate on operational matters but cannot generate legitimacy for the broader system.
Academic-first governance coordinates more cleanly because mission narratives and internal norms reduce negotiation costs. That advantage becomes fragile if external pressure forces convergence toward the Power Two model. The legitimacy buffer is real but not infinite.
Mid-major coordination sits near breakdown. Low revenue magnifies incentives to defect through informal deals, while enforcement attention remains inconsistent. These programs face the worst combination: high pressure to compete, low resources to professionalize, and elevated exposure as potential test cases for regulators.
Coase Vision Prediction
A single national focal point will not emerge absent congressional legitimacy. A multi-regime equilibrium will form: Power Two governance becomes quasi-standard, academic-first schools attempt principled separation, and mid-majors drift into opportunistic variance.
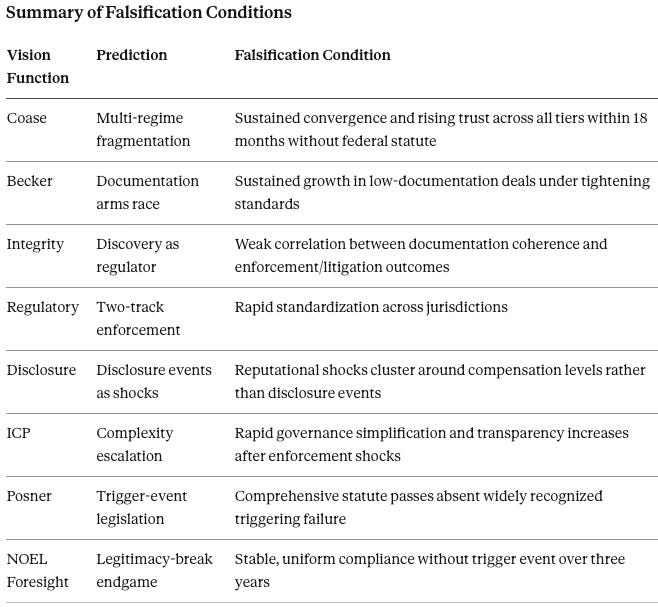
Falsification contract: Coordination should strengthen across all tiers within eighteen months without a federal statute. Sustained convergence and rising trust would falsify the fragmentation forecast.
IV.B. Becker Vision: Incentive Exploitation After Coordination Strain
Chicago diagnosis: Incentives re-optimize once coordination degrades.
Once coordination degrades, incentives rather than norms drive behavior. The Becker Vision CDT foresight simulation models how rational actors exploit the system, how fast exploitation spreads, and through which channels it operates. The question is not whether exploitation will occur but who exploits, at what scale, and with what documentation.
Interpretation
High-revenue schools will search for above-cap advantage using layered entities, marketing deliverables, and donor structures that mimic commercial sponsorship. The highest payoffs sit in ambiguity, so actors will push the boundary until enforcement credibly bites.
Collectives face a sorting event. Sophisticated collectives will professionalize documentation and pivot toward brand-safe pipelines. Booster-cash collectives will remain, but enforcement and reputational risk will compress their scale. The collective ecosystem will stratify into audit-ready vehicles and legally exposed holdouts.
Brands will keep moving money toward measurable deliverables with clear business purposes. Private capital will invest selectively, demanding governance clarity and auditability before entry. Capital will discipline the system, not accelerate it.
Becker Vision Prediction
A documentation arms race will emerge. A small set of institutions and intermediaries will build high-compliance monetization machines; a larger set will run thin paperwork and accept rising litigation and enforcement exposure.
Falsification contract: Booster-cash models should not expand materially under tightening standards. Sustained growth in low-documentation deals would falsify the capital discipline forecast.
IV.C. Integrity Vision: Structural Coherence Under Pressure
Chicago diagnosis: Institutional integrity reveals whether Beckerian exploitation has outrun stated governance rationales.
The Integrity Vision CDT foresight simulation tests whether institutions maintain coherent governance when incentives spike. Integrity here does not mean ethics in an abstract sense. It means alignment between stated policies, internal practices, and discoverable documentation. Integrity failures become visible when narratives contradict records.
Interpretation
Integrity failures will not look like open defiance. They will look like sophisticated stories that fail discovery: valuation memos that do not match internal communications, deliverables that do not match payments, and governance sign-offs that exist only to create plausible deniability.
Academic-first institutions hold a legitimacy buffer, but lag risk matters. A late shift into market mimicry without a coherent educational rationale will trigger reputational shock and potential antitrust scrutiny. The worst outcome for these schools is quiet convergence followed by sudden exposure.
Integrity Vision Prediction
Discovery risk will become the real regulator. Courts and state enforcement will punish narrative-document gaps more than headline compensation numbers.
Falsification contract: Enforcement and litigation outcomes should correlate with documentation coherence. Weak correlation would falsify the narrative-document mechanism.
IV.D. Regulatory Vision: Enforcement Behavior and Jurisdictional Fragmentation
Chicago diagnosis: Fragmented enforcement creates the doctrinal and feedback lag that makes Posnerian correction late.
The Regulatory Vision CDT foresight simulation models enforcement cycles, patchwork dynamics, and coalition behavior among the bodies responsible for NIL oversight. Enforcement legitimacy depends on consistency, due process, and perceived fairness. In the interregnum, all three are contested.
Interpretation
Enforcement will struggle to look legitimate without uniform statutory authority. State transparency requirements and political incentives will pull the system toward disclosure conflicts and forum selection games.
Selective enforcement is the central legitimacy risk. Visible exceptions for powerful programs will collapse compliance incentives for everyone else. If elite schools can defect without consequence, mid-majors will stop taking compliance seriously.
Regulatory Vision Prediction
A two-track enforcement reality will form: high-visibility cases to signal toughness and a broad under-enforced gray zone where practices drift until a triggering scandal or lawsuit forces action.
Falsification contract: Enforcement should remain uneven across states and conferences. Rapid standardization across jurisdictions would falsify the fragmentation forecast.
IV.E. Disclosure Vision: Transparency, Drip Timing, and Narrative Blowback
Chicago diagnosis: Disclosure events function as coordination shocks that make previously hidden exploitation legible.
In the interregnum, what becomes visible often matters more than what is illegal. The Disclosure Vision CDT foresight simulation predicts where secrecy creates liability and reputational cascades.
Interpretation
Secrecy will not hold. Public records laws, whistleblowers, contract disputes, and discovery will produce staggered disclosures. Drip timing will shape perception—partial releases will look like concealment even when lawful.
Brands will pressure the ecosystem toward clarity because they cannot tolerate reputational risk from association with opaque structures. Schools and collectives that refuse transparency will experience repeated reputational resets.
Disclosure Vision Prediction
A small number of high-profile leaks will function like enforcement events, triggering copycat litigation and rapid policy tightening.
Falsification contract: Reputational shocks should cluster around disclosure events rather than compensation levels. A compensation-only pattern would falsify the disclosure thesis.
IV.F. Institutional Cognitive Plasticity Vision: Adaptation Versus Doubling Down
Chicago diagnosis: Institutional plasticity determines whether actors can exit the Coase→Becker trap or become locked in.
The ICP Vision CDT foresight simulation assesses whether institutions can update their governance architecture when exposed or whether they respond by adding complexity and defending legacy structures. The interregnum rewards institutions that learn; it destroys those that ossify.
Interpretation
Congress will not provide rapid corrective learning. That constraint forces the settlement infrastructure and institutions to evolve internally or fail.
High-revenue universities will prefer continuity until a crisis forces change. Academic-first institutions will adapt earlier because they can defend mission-based boundaries and implement simpler governance structures.
Institutional Cognitive Plasticity Vision Prediction
The most dangerous period will occur after the first enforcement shocks. Low-plasticity institutions will respond by layering more complexity rather than simplifying governance, increasing discovery risk.
Falsification contract: Low-plasticity institutions should escalate complexity after enforcement shocks. Rapid governance simplification and transparency increases would falsify the doubling-down forecast.
IV.G. Posner Vision: Legal Correction Capacity Within the Harm Window
Chicago diagnosis: Legal correction lags when the learning environment turns wicked.
The Posner Vision CDT foresight simulation determines whether law can correct the system before it locks into a harmful equilibrium. Correction requires that courts, agencies, or Congress act faster than institutions can adapt around enforcement. In the interregnum, avoider capacity is high.
Interpretation
Courts and agencies can correct, but timing will lag behavior. Avoider capacity is high: institutions can route payments through complex structures faster than doctrine can update.
Congress will re-enter only after politically salient failure. That means litigation and agency signaling will carry the interim system until a triggering event shifts political incentives.
Posner Vision Prediction
A correction window will open only after a visible legitimacy break: selective enforcement, a major leak, or an employment classification shock. The first durable federal template will likely include conditional safe harbor design features because the system will demand auditability.
Falsification contract: A comprehensive statute should not pass absent a widely recognized triggering failure. Calm legislative success would falsify the trigger-event thesis.
IV.H. Integrated Foresight Vision: Scenario Analysis
Chicago diagnosis: The interregnum ends through the Coase→Becker→Posner sequence—the question is which stage dominates the exit.
The MCAI Foresight Vision integrates all vectors into forward scenarios with time-sequenced predictions and early-warning indicators. The purpose is not to predict the future with certainty but to identify the most probable pathways and the signals that indicate which pathway the system is entering.
Scenario Set
Scenario 1: Coase Fragmentation Persists (Patchwork Persistence). The settlement infrastructure remains live, enforcement stays uneven, and the market stratifies by compliance sophistication. Coordination capacity remains degraded but stable. No single shock forces resolution. Duration: potentially indefinite.
Scenario 2: Becker Exploitation Dominates (Legitimacy Collapse). Selective enforcement combined with high-profile leaks destroys compliance incentives. Rational actors openly defect because exploitation yields higher returns than compliance. The system loses coherence.
Scenario 3: Posner Correction Arrives Late (Employee Classification Cascade). Litigation and agency posture shift the labor frame. Courts rule that control-plus-pay facts constitute employment—but only after years of interim practices have created retroactive liability exposure.
Scenario 4: Conditional Federal Re-Entry. Congress returns with legislation featuring audits, mandatory disclosure, and bounded antitrust immunity tied to compliance benchmarks. Sovereign legitimacy restoration interrupts the Coase→Becker→Posner cycle.
Scenario 5: Durable Settlement Governance. Enforcement legitimacy improves enough that the settlement infrastructure stabilizes as the de facto regulatory regime without federal intervention. Coordination capacity rebuilds through repeated interaction.
Early-Warning Indicators
The following signals indicate which scenario is becoming dominant:
Rising litigation that targets documentation and valuation rather than headline amounts suggests patchwork persistence is hardening into stratification
Public records conflicts that create drip-disclosure cascades signal legitimacy collapse risk
Enforcement actions that appear to exempt elite programs accelerate legitimacy collapse
Rapid professionalization of documentation among top collectives indicates capital discipline is working
Title IX distribution controversies that become politically salient could trigger federal re-entry
Agency signaling on employment classification (DOL, NLRB) accelerates the classification cascade scenario
System Prediction
The interregnum will end through a legitimacy break, not through quiet convergence. A trigger event will force either court-built labor rules or conditional federal intervention.
Falsification contract: Stable, uniform compliance without a trigger event over three years would falsify the legitimacy-break endgame.
The most likely near-term outcome is patchwork persistence with increasing stratification. The system will not collapse immediately, but it will not stabilize either. The question is which trigger event arrives first and how institutions have positioned themselves when it does.
V. How Universities Will Respond
The simulation outputs presented in Section IV describe system-level dynamics, but institutions must act at the organizational level. The following analysis translates the foresight findings into predictions about how universities will actually behave during the interregnum. The behavioral patterns described here emerge from the incentive structures, coordination constraints, and legitimacy pressures identified in the Vision Function analysis. Understanding these response patterns is essential for any actor—whether university leader, policymaker, or athlete—seeking to anticipate how the system will evolve.
Institutional Behavior Under Sustained Ambiguity
Universities will not wait for Congress. They will experiment, differentiate, and quietly coordinate, because survival incentives now operate on shorter cycles than legislation. The responses cluster into predictable strategies, with creativity rising as legitimacy weakens.
Strategy 1: Internal Solutions Before National Ones
Universities will try to solve NIL locally and institution-specifically, not system-wide. National solutions require legitimacy they do not control. The predictable response is to build internal governance that creates plausible deniability if enforcement fragments.
What this looks like in practice:
Creation of central NIL review offices with valuation guidelines and compliance sign-off
Internal “clearing” committees that approve deals before submission to settlement mechanisms
Standardized contract templates to reduce discovery risk
Formal separation between athletic departments and donor-linked entities on organizational charts
Why this happens: Local governance gives plausible deniability. If enforcement fragments, institutions want to say, “We exercised independent judgment.”
Risk: Peer-mirroring of internal policies can still look collusive if documents or communications show coordination.
Strategy 2: Legal Creativity, Not Cash Creativity
Universities will not get more creative about how much they pay. They will get more creative about how payments are justified and structured. Discovery punishes incoherent stories. Creativity will focus on auditability and narrative alignment, not raw compensation.
Expected design patterns:
Expansion of content-creation studios embedded in athletics or communications departments
Licensing and intellectual property-based NIL structures tied to media archives, social content, or educational programming
Tiered deliverables tied to marketing reach rather than athletic performance
Bundling NIL with academic or experiential components that support “educational mission” narratives
Failure mode: Over-engineering. Excessive complexity increases the chance that internal emails contradict public rationales.
Strategy 3: Selective Capital Partnerships
Universities will not openly “partner with private equity” in NIL. They will allow capital to orbit the system through intermediaries. Capital will discipline the ecosystem rather than accelerate it.
Where capital will enter:
Media rights extensions and content platforms
Athlete-branding platforms with scalable documentation
Data, analytics, and compliance infrastructure vendors
Revenue-sharing vehicles tied to intellectual property rather than payroll
What capital will avoid:
Booster-style collectives without governance
Direct athlete payroll exposure
Structures that look like employment substitution
Key insight: Schools that attract capital will be those that simplify governance and professionalize NIL operations early. Capital will not rescue chaos.
Strategy 4: Self-Regulation Through Risk Management
Universities will stop appealing to “amateurism” or “tradition.” They will self-regulate through risk management logic. The language will shift from “protecting the student-athlete experience” to “documenting the business rationale.”
Self-regulation tools that will emerge:
Internal compensation bands justified by market comparables
Deal-level documentation scoring systems
Title IX distribution monitoring dashboards
Periodic internal audits designed for future discovery rather than public release
What self-regulation is not: It is not altruistic. It is not uniform. It is not transparent by default. It is defensive governance designed to survive legal scrutiny.
Differentiation by Institutional Type
Power Two Schools will push the envelope first, centralize governance, tolerate higher legal risk in exchange for competitive advantage, and retreat only after visible enforcement or litigation losses.
Academic-First Institutions will resist convergence longer, lean heavily on mission-aligned narratives, and face reputational risk if they quietly adopt market mimicry later. Their advantage is principled independence; their risk is being dragged into convergence through conference realignment pressure.
Mid-Major Programs will struggle the most. They will oscillate between underpayment risk and informal workarounds. Regulators or plaintiffs seeking precedent may target them as test cases. Their constraint is resources; their exposure is visibility as enforcement targets.
What Universities Will Not Do
Universities will not wait passively for Congress. They will not agree to true national standards without statutory protection. They will not share sensitive NIL governance data voluntarily. They will not publicly acknowledge coordination incentives even when coordination is occurring.
Universities will respond to the interregnum the way complex institutions always respond to legal ambiguity: localize control, professionalize justification, invite capital only where it disciplines risk, and self-regulate quietly and defensively. The system will look orderly on the surface and highly strategic underneath. The section that follows translates these dynamics into guidance for specific actors navigating the interregnum.
VI. Implications by Audience
The preceding sections analyzed system dynamics and institutional behavior at an aggregate level. The guidance that follows translates those findings into actionable recommendations for specific actors.
For University Presidents
The interregnum places presidents in a governance position without precedent. You are operating a revenue-generating athletic enterprise under contested legal authority, fragmented enforcement, and sustained public scrutiny. The strategic imperative is to build institutional architecture that survives discovery, adapts to enforcement shocks, and does not depend on congressional rescue.
The core challenge: NIL governance now carries board-level risk. Documentation failures, selective enforcement, and disclosure events can trigger reputational damage, litigation exposure, and regulatory scrutiny that escalates beyond the athletic department. The traditional delegation model—let the AD handle sports—does not insulate the institution when the underlying governance regime lacks legitimacy.
Priority actions:
Ensure NIL governance reports to a senior officer with legal and fiduciary oversight, not just athletic department leadership
Require documentation standards that assume every internal communication may become public
Prepare a narrative rationale for your institution’s NIL approach that is distinct from peer institutions and grounded in mission
Model scenarios for enforcement shock, employment classification, and disclosure events before they occur
Strategic insight: The institutions that emerge strongest from the interregnum will be those that built defensible governance architectures before enforcement tested them. Reactive governance after a disclosure event or enforcement action costs far more than proactive design.
For Athletic Directors
You are the operational node where policy meets implementation. The interregnum rewards athletic directors who professionalize NIL operations and punishes those who rely on informal relationships and undocumented arrangements. Compliance is no longer about following NCAA rules; it is about surviving litigation and regulatory scrutiny.
The core challenge: The relationships that made you effective in the old system—close ties with boosters, informal understandings with coaches, handshake deals with collectives—are now liability vectors. Professionalization requires creating formal distance from the same networks that fund competitive success.
Priority actions:
Build or acquire internal NIL review capacity with valuation expertise and market comparables
Standardize contract templates and approval workflows with clear audit trails
Create formal separation between your office and donor-linked collectives, even when relationships are close—document the independence
Track Title IX distribution metrics proactively, not reactively, and prepare defensible rationales for any disparities
Operational insight: The ADs who navigate the interregnum successfully will be those who can maintain competitive NIL positioning while building governance infrastructure that survives enforcement scrutiny. Speed and documentation are not trade-offs; they are complements.
For General Counsels
You are the risk manager for an institution operating in a low-legitimacy enforcement environment. The traditional compliance model—follow the rules and document adherence—does not apply when the rules are contested and the enforcers lack authority. Your role is to anticipate discovery, prepare for litigation, and advise on governance structures that survive scrutiny.
The core challenge: Narrative-document coherence is now the primary liability vector. The gap between what institutions say publicly about NIL and what internal communications reveal will determine litigation outcomes, enforcement targeting, and reputational damage. Your job is to close that gap before discovery opens it.
Priority actions:
Audit existing NIL arrangements for narrative-document coherence—identify gaps between stated rationales and internal communications
Prepare privilege protocols for NIL-related communications before they become litigation targets
Monitor litigation trends and enforcement patterns for early signals of regulatory strategy
Advise institutional leadership on disclosure timing, public records exposure, and the reputational cost of drip-release scenarios
Litigation insight: The first wave of NIL litigation will target documentation failures and valuation inconsistencies, not headline compensation numbers. Institutions with clean paper trails will have defensible positions; those with informal arrangements will face discovery risk that compounds over time.
For Lawmakers
The interregnum exists because you did not act. The settlement infrastructure now carries governance weight that its designers never intended it to bear. The longer the vacuum persists, the more the system stratifies into audit-ready elites and legally exposed laggards. Federal intervention will eventually become necessary, but the trigger will be failure, not foresight.
What will force action:
A high-profile employment classification ruling that reframes NIL as wages
A Title IX enforcement scandal with political salience
A legitimacy collapse that damages public confidence in college athletics
State-level fragmentation that creates compliance impossibility for multi-state programs
What durable legislation will require:
Conditional safe harbor tied to compliance benchmarks and auditability
Mandatory disclosure and audit mechanisms with enforcement teeth
Bounded antitrust immunity that does not shield all institutional behavior
Preservation pathways for academic-first institutions and Olympic sports models
Political insight: The member who sponsors comprehensive NIL legislation after a triggering failure will receive credit for solving a crisis. The member who sponsors it before the failure will face industry opposition and constituent indifference. The asymmetry explains the stalemate and predicts its resolution.
For High-Potential Athletes
You are operating in a system where your leverage depends on documentation, representation quality, and institutional context—not just your athletic performance or social media following. The interregnum rewards athletes who professionalize their NIL approach and punishes those who rely on informal promises or undocumented arrangements. The same coordination failure that creates opportunity also creates risk.
The core challenge: NIL governance is contested, enforcement is inconsistent, and the rules may change retroactively. Arrangements that seem safe today may become liabilities if employment classification shifts or if enforcement tightens on “valid business purpose” requirements. Athletes who treat NIL as a transactional afterthought will bear disproportionate risk when the system corrects.
Priority actions:
Secure representation from advisors who understand compliance requirements, not just deal volume—ask specifically about their documentation practices and settlement compliance protocols
Ensure every NIL arrangement has written terms, clear deliverables, and documented business purpose that would survive regulatory scrutiny
Understand the difference between settlement-compliant direct pay (institution-controlled, capped) and collective-mediated deals (intermediary risk, documentation variance)
Evaluate institutions partly on their NIL governance sophistication, not just their NIL spending—the highest-paying programs may also carry the highest retroactive liability risk
Maintain your own records of deliverables performed, payments received, and communications with institutions and collectives
Risk awareness: Informal arrangements that lack documentation create exposure for you, not just for the institution. If enforcement tightens or classification shifts, you may face disputes over payments you thought were settled. Litigation and enforcement actions have already named athletes as parties; do not assume institutions will shield you from consequences.
Leverage insight: The interregnum creates asymmetric information—you may know more about your market value than institutions operating under cap constraints. Use that leverage strategically, but document the business rationale for every arrangement. Your negotiating position is stronger when your compliance posture is clean.
Every actor in the system faces distinct pressures in the interregnum. The common thread is that documentation, narrative coherence, and adaptive capacity now matter more than raw spending or traditional compliance frameworks.
VII. Consolidated Takeaways
The simulation findings distill into a unified picture of what the analysis reveals and what it implies for action. The purpose is not to simplify the complexity but to identify the through-lines that matter most for institutional decision-making.
What the Simulation Reveals
A functioning interim regime exists, but legitimacy remains contested. The settlement infrastructure provides operational coherence without political legitimacy. Coordination holds at the top tier and weakens quickly outside it. Incentives push behavior toward boundary-testing until enforcement becomes credible.
Disclosure events will act like regulatory shocks. In a low-legitimacy environment, what becomes visible often matters more than what is illegal. Institutional adaptation will separate resilient actors from those that double down and get trapped in complexity.
The interregnum will not end through quiet convergence. It will end through a legitimacy break that forces either court-built rules or conditional federal intervention.
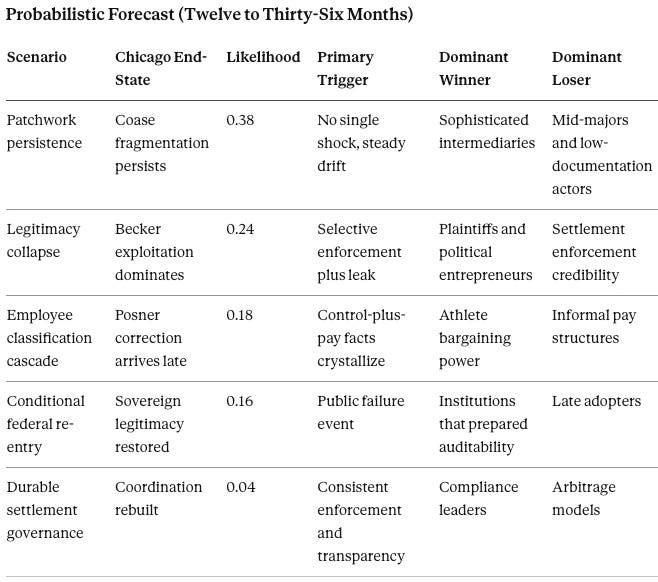
Probabilistic Scenario Forecasts (Twelve to Thirty-Six Months)
Patchwork persistence (38% likelihood). The settlement infrastructure remains live, enforcement stays uneven, and the market stratifies by compliance sophistication. No single shock forces resolution. Sophisticated intermediaries and audit-ready collectives capture increasing market share. Mid-major programs and low-documentation actors face elevated enforcement risk as potential test cases. Duration: potentially indefinite until a trigger event emerges.
Legitimacy collapse (24% likelihood). Selective enforcement combined with high-profile leaks—public records requests, whistleblower disclosures, or litigation discovery—destroys compliance incentives. Rational actors openly defect because exploitation yields higher returns than compliance. Plaintiffs and political entrepreneurs gain leverage; settlement enforcement credibility collapses. The CSC’s contractual authority proves insufficient to hold the system together.
Employee classification cascade (18% likelihood). Litigation and agency posture shift the labor frame. Courts rule that control-plus-pay facts constitute employment—but only after years of interim practices have created retroactive liability exposure. DOL and NLRB signaling accelerates the timeline. Athlete bargaining power increases substantially; informal pay structures face legal exposure; institutions that treated athletes as independent contractors face back-pay claims.
Conditional federal re-entry (16% likelihood). A public failure event—a major enforcement scandal, a Title IX distribution controversy that becomes politically salient, or a court ruling that destabilizes the settlement—forces Congress to return. Legislation features audits, mandatory disclosure, and bounded antitrust immunity tied to compliance benchmarks. Institutions that prepared auditability survive the transition; late adopters face restructuring costs and potential liability.
Durable settlement governance (4% likelihood). Enforcement legitimacy improves enough that the settlement infrastructure stabilizes as the de facto regulatory regime without federal intervention. Consistent CSC enforcement, transparency improvements, and voluntary compliance create a coordination equilibrium. Compliance leaders gain competitive advantage; arbitrage models compress. Requires sustained institutional commitment to legitimacy—the least likely outcome given current incentive structures.
Practical Guidance
Universities should treat documentation coherence as a first-order risk control. Every NIL arrangement must withstand discovery scrutiny.
Conferences should avoid peer-mirroring that looks like coordinated wage setting. Independent rationale, even if it reaches similar numbers, provides legal insulation.
Enforcement bodies should prioritize consistency and due process to preserve legitimacy. Selective enforcement will collapse the system faster than non-enforcement.
Market actors should expect stratification. Audit-ready channels will capture increasing share of NIL money. Booster-cash models will compress.
Athletes should professionalize their representation and documentation. The interregnum rewards those who operate like businesses.
The interregnum is a temporary governance regime under strain. Stability will persist until a trigger event forces a reset. How institutions position themselves before that trigger determines who survives the transition.
Appendix: Falsification Contracts
Foresight analysis that cannot be tested is not analysis—it is speculation. The appendix collects the falsification contracts embedded throughout the simulation into a single reference, allowing readers to evaluate the analysis against observed outcomes over time. Each contract specifies conditions that would falsify the corresponding prediction, requiring revision of the underlying causal model. The commitment to testability distinguishes rigorous foresight from advocacy or prediction theater.
Methodology Note
The simulation commits to conditions that would falsify its predictions. Falsification contracts are not hedges; they are epistemic commitments that allow testing against observed outcomes. If the system behaves contrary to the predictions without intervening external shocks, the simulation’s causal model requires revision.
These falsification contracts allow readers to evaluate the simulation against observed outcomes. The analysis succeeds if the predicted patterns emerge; it requires revision if falsification conditions are met.
Sources Appendix: Prior MindCast AI Publications
The following citations cover MindCast AI publications referenced in the simulation. These publications form the analytical foundation on which the Interregnum simulation builds.
2025 Publications
Group 1: Congressional Legislative Analysis
MCAI Lex Vision: SAFE vs. SCORE Act — Which Path Should Define NCAA NIL? (September 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/ncaasafeact
MCAI Lex Vision: How the SCORE Act Codifies College Sports Inequality (August 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/scorecantwellletter
MCAI Lex Vision: Foresight Simulation of the SCORE Act and NCAA Settlement (July 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/scoreact
These publications evaluate competing congressional approaches to NIL legislation, analyzing the structural differences between the SCORE Act and SAFE Act frameworks and their implications for institutional compliance. The series introduced conditional safe harbor as a legislative design principle and identified structural brittleness in static compliance frameworks.
Group 2: Settlement and Antitrust Foundations
MCAI Lex Vision: The NCAA NIL Settlement, Foresight Realized (June 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/ncaasettlement
MCAI Lex Vision: Restructuring the NCAA Name-Image-Likeness Settlement (May 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/ncaa-nil
MCAI Lex Vision: US DOJ Participation in Zeigler v. NCAA, Strategic Impact (June 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/zeiglerdoj
MCAI Lex Vision: AI-Era Anticipatory Antitrust for NCAA NIL Compliance (July 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/ncaaai
These publications traced the dismantling of amateurism through litigation, modeled the House v. NCAA settlement structure, and analyzed federal enforcement posture shifts—including DOJ signaling toward institutional deference. The series revealed structural antitrust risks hidden from conventional legal reporting and established the analytical foundation for understanding settlement-based governance.
Group 3: Institutional Governance and Compliance
MCAI Lex Vision: Executive Foresight and the New Era of NCAA Institutional NIL Legitimacy (July 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/ncaaeo
MCAI Lex Vision: Navigating the NCAA NIL Compliance Matrix — University of Washington Analysis (July 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/uwnil
MCAI Lex Vision: National Name-Image-Likeness Simulation Framework (July 2025) https://www.mindcast-ai.com/p/ncaaantitrustsnapshot
These publications applied Cognitive Digital Twin methodology to specific institutional contexts, evaluating universities across tiered risk matrices and simulating how executive action and settlement requirements interact with university governance strategies. The series demonstrated how foresight simulation translates system-level dynamics into institution-specific compliance guidance.