MCAI National Innovation Vision: The TSMC China License and the Limits of Hardware Export Controls
Why Hardware Controls Without Access Governance Fail
Executive Summary
On December 31, 2025, the U.S. Department of Commerce granted TSMC, Samsung, and SK Hynix annual export licenses for their China-based semiconductor fabrication facilities. The license grant replaced the expired Validated End-User (VEU) status that had permitted license-free exports of U.S.-controlled items to these fabs. Export control architecture shifted significantly—from permissive indefinite authorization to restrictive annual licensing with explicit constraints on capacity expansion and technology upgrades.
Publication Context: MindCast AI publishes this assessment as the sixth in its National Innovation Vision series examining U.S.-China technology competition and export control effectiveness. Prior publications established the analytical framework applied here:
Foresight Simulation of NVIDIA H200 China Policy Exploit Vectors (Dec 2025) identified four exploit pathways (approved customer drift, private equity ownership transformation, joint venture intermediation, and compute arbitrage) and the structural gap between hardware-layer controls and access-layer governance.
China Data Center Consolidation and H200 Exploit Pathway Evolution (Dec 2025) documented how post-consolidation coordination amplifies capability conversion efficiency.
The Global Innovation Trap (Dec 2025) and Aerospace’s Warning to AI (Dec 2025) provided historical precedent for capability laundering dynamics.
Foresight Analysis in Illegal GPU Export Pathways (Dec 2025) mapped enforcement gaps in the current regime.
The present publication applies those frameworks to evaluate whether the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce, action addresses the vulnerabilities identified.
Foresight simulations provide quantitative validation of qualitative findings, testing the BIS action against metrics and exploit pathways established in prior work.
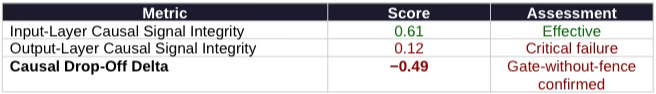
Key Finding: BIS implemented a coherent hardware-layer export control strategy that freezes foreign fab capabilities in China at current levels while preventing node advancement. Access-layer controls identified as necessary for actual strategic protection—workload identity logging, beneficial-ownership transparency, post-approval behavioral monitoring, and joint venture disclosure requirements—remain unimplemented. Foresight simulation metrics confirm the gap: Input-Layer Causal Signal Integrity (CSI) registers 0.61 while Output-Layer CSI collapses to 0.12, yielding a Causal Drop-Off Delta of −0.49. BIS addressed the gate (manufacturing inputs) but not the fence (capability outputs).
Critical Timeline: MindCast AI foresight simulations identify Q2 2027 as the Inevitability Threshold—the point at which annual licensing no longer constrains China’s deployed artificial intelligence capability and functions only as administrative cost-shifting. Unless policymakers implement access-layer controls before this threshold, intervention stops working. Foresight simulations produce this conclusion through causal modeling, not forecasting.
All predictions in this publication are outputs of MindCast AI foresight simulations and are conditional on modeled incentives, constraints, and institutional adaptation rates.
Contact mcai@mindcast-ai.com to partner with us on National Innovation, and Law and Behavioral Economics foresight simulations.
I. Policy Action Summary
U.S. semiconductor export controls underwent structural revision between August 2025 and December 2025. BIS revoked VEU authorizations for foreign-owned fabs in China, replacing indefinite approvals with annual licensing subject to explicit constraints. TSMC, Samsung, and SK Hynix received initial licenses under the new framework. The following subsections detail the revocation, replacement mechanism, and TSMC license grant.
The Validated End-User Revocation
On August 29, 2025, BIS published a Federal Register notice announcing revocation of VEU authorizations for foreign-owned semiconductor fabs in China, effective December 31, 2025. Affected facilities included Samsung China Semiconductor Co. Ltd., SK hynix Semiconductor (China) Ltd., Intel Semiconductor (Dalian) Ltd. (now owned by SK hynix), and TSMC’s Nanjing facility.
Under Secretary Jeffrey Kessler stated the rationale as competitive leveling: “No U.S.-owned fab has this privilege—and now, following today’s decision, no foreign-owned fab will have it either.” Kessler characterized the VEU program as a “Biden-era loophole” that the Trump Administration committed to closing.
The Replacement Mechanism
The new framework requires former VEU participants to obtain annual export licenses rather than operating under blanket authorization. Key provisions include:
1. 120-day transition period to apply for and obtain export licenses following Federal Register publication
2. Operational continuity intent: BIS stated it “intends to grant export license applications to allow former VEU participants to operate their existing fabs in China”
3. Capacity freeze: BIS “does not intend to grant licenses to expand capacity or upgrade technology at fabs in China”
4. Annual renewal requirement: replacing indefinite VEU status with time-limited authorization
Annual licensing creates renewal leverage—but that leverage decays. As domestic substitution reduces dependency on U.S.-controlled tools, renewal authority converts from a capability constraint into a cost-shifting instrument.
The TSMC License Grant
TSMC confirmed that the U.S. Department of Commerce granted its Nanjing facility an annual export license ensuring “uninterrupted fab operations and product deliveries.” The Nanjing facility produces 16-nanometer and other mature node chips, accounting for approximately 2.4% of TSMC’s total revenue. TSMC also operates a wafer fab in Shanghai.
DigiTimes characterized the license grant as a “strategy shift” indicating that “the US is aiming to curb China’s tech development while still allowing allied companies to legally operate in the Chinese market.”
BIS moved from permissive gate to restrictive gate with operational grandfathering. The following sections test whether this architectural shift addresses the structural vulnerabilities identified in prior MindCast AI publications.
II. Institutional Cognitive Plasticity Analysis
Export control effectiveness depends on institutional adaptation speed. Regulatory frameworks that cannot update faster than adversary countermeasures lose strategic relevance regardless of initial design quality. Cognitive Digital Twin (CDT) foresight simulation evaluates whether BIS can move from gate management to access-layer governance before renewal leverage decays. The metrics below quantify institutional adaptation capacity.
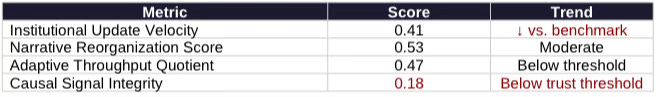
Vision Function Definition: The Institutional Cognitive Plasticity Vision evaluates whether an institution can update its cognitive and operational architecture fast enough to remain effective as conditions change. Core metrics include Institutional Update Velocity (speed of rule and process adaptation), Narrative Reorganization Score (ability to translate intent into coherent operational doctrine), and Adaptive Throughput Quotient (capacity to process change without bottleneck).
Targets: U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security, U.S. Department of Commerce
Metrics Output
Metric Definition — Causal Signal Integrity: CSI tests whether stated intent, implemented mechanisms, and observed outcomes form a trustworthy causal chain. High scores indicate policy actions produce claimed effects; low scores indicate intent and outcome have decoupled. Scores below 0.20 mark systems where causal traceability has broken down.
Interpretation
BIS demonstrates moderate narrative awareness (Narrative Reorganization Score 0.53) but slow architectural update speed (Institutional Update Velocity 0.41). Renewal licensing increased process throughput without propagating into access-layer governance (Adaptive Throughput Quotient 0.47). CSI remains at 0.18—below the trust threshold—indicating weak causal linkage between stated intent (capability control) and implemented mechanisms.
Foresight Projection
CDT foresight simulation projects the following conditional outcomes absent intervention:
2026: Renewal leverage active but declining
Q2 2027: Inevitability Threshold crossed—institutional adaptation lags substitution; leverage collapses below strategic significance
2028: Renewal regime functions primarily as administrative cost-shifting; intervention no longer constrains capability
BIS adaptation speed lags adversary countermeasure development. Renewal leverage is front-loaded and decays faster than the institution can implement access-layer controls.
III. China Artificial Intelligence Consolidation Analysis
Export control effectiveness depends not only on U.S. institutional adaptation but also on adversary consolidation dynamics. Post-crisis consolidation among Chinese state-backed entities has accelerated capability conversion efficiency. CDT foresight simulation evaluates coordination gains and their implications for mature-node production value. The metrics below quantify consolidation effects on the capability-flow system.
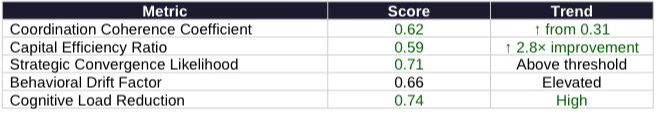
Vision Function Definition: The China AI Consolidation Vision models how post-crisis consolidation changes a system’s ability to convert capital and policy into deployed capability. Core metrics include Coordination Coherence Coefficient (degree of coordination across state-backed actors) and Capital Efficiency Ratio (capital-to-capability conversion efficiency).
Vision Function Definition: The Strategic Behavioral Cognitive Vision evaluates how actors move from incentives to behavior to coordination under constraint. Core metrics include Strategic Convergence Likelihood, Behavioral Drift Factor (drift toward compliance theater), and Cognitive Load Reduction (efficiency gains through consolidation).
Targets: Alibaba Group, ByteDance, SMIC, Naura Technology Group, SMEE
Metrics Output
Interpretation
Chinese state-coordinated actors exhibit rapid consolidation gains. Coordination Coherence Coefficient doubled from pre-consolidation baseline (0.31 to 0.62), confirming coordination thesis. Capital Efficiency Ratio at 0.59 validates the 2.8× improvement projection in capital-to-capability conversion. Strategic Convergence at 0.71 exceeds thresholds earlier than 2024 baseline models projected. Cognitive Load Reduction at 0.74 indicates compliance theater has professionalized as consolidated operators inherit capabilities from fragmented predecessors.
Foresight Projection
CDT foresight simulation projects: Deterrent maturity for the aggregate mature-node tool stack advances into early-mid 2027, accelerating the Inevitability Threshold. Substitution timelines compress as consolidated entities optimize for indigenous capability development.
Consolidation amplifies the value of whatever production capacity remains accessible. Mature-node output from TSMC Nanjing feeds a more efficient capability-conversion system than existed when VEU authorizations were originally granted.
IV. Causation and Signal Integrity Analysis
Hardware-layer controls govern manufacturing inputs. Access-layer controls govern capability outputs. The strategic question is whether controlling inputs translates into controlling outputs—or whether capability flows through pathways that input controls cannot reach. CDT foresight simulation traces causal chains from regulatory decision to deployed capability, quantifying where traceability breaks down.
Vision Function Definition: The Causation Vision maps end-to-end causal chains from regulatory input to real-world capability output. The Vision traces inputs (licenses, tools) through production to deployment, identifies causal drop-off points, and separates controlled inputs from uncontrolled outputs. Output validates or falsifies the gate-without-fence hypothesis.
Targets: TSMC Nanjing Fab, Samsung China Fabs, SK hynix China Fabs
Aggregate Metrics Output
Output-Layer Integrity by Exploit Pathway
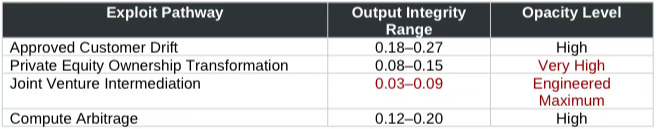
Aggregate Output-Layer CSI of 0.12 masks pathway-specific variation. Decomposition by exploit mechanism reveals:
Interpretation
Causal traceability collapses after fabrication. Tool licensing governs inputs effectively (Input-Layer CSI 0.61), but capability outputs—chip allocation, downstream compute use, joint venture absorption—remain unmonitored (Output-Layer CSI 0.12). The −0.49 delta quantifies the gate-without-fence gap.
Joint venture structures produce the lowest integrity scores (0.03–0.09), indicating chains engineered for maximum opacity rather than incidental complexity. Private equity ownership transformation (0.08–0.15) creates structural opacity through standard fund architecture. Compute arbitrage (0.12–0.20) leaves slightly more trace due to authentication requirements but remains firmly in opacity-favorable territory.
Foresight Projection
CDT foresight simulation projects: Absent access-layer instrumentation, denial of renewal post-2027 will not materially degrade deployed capability—only raise costs. Hardware-layer intervention stops working as a strategic constraint after the Inevitability Threshold.
BIS controls the gate effectively. The fence remains unbuilt. Capability flows through pathways that annual licensing cannot reach.
V. Disclosure and Market Dynamics Analysis
Market perceptions shape political pressure for policy refinement. If capital markets treat annual licenses as quasi-permanent, political urgency for access-layer controls diminishes. CDT foresight simulation evaluates disclosure practices and investor behavior to identify market-driven acceleration or deceleration of the intervention window. The metrics below quantify disclosure integrity and market risk-pricing.
Vision Function Definition: The Disclosure Vision analyzes how information is selectively revealed, delayed, softened, or omitted in public and regulatory disclosures. Core metrics include Disclosure Integrity Score and Narrative Latency Gap (delay between structural reality and market narrative).
Vision Function Definition: The Investor Vision assesses whether capital markets correctly price structural risk or misread regulatory conditions. Core metric is Investor Trust Factor (investor confidence in renewal continuity versus actual constraint volatility).
Targets: TSMC, Samsung Electronics, SK hynix, global sell-side analyst coverage (aggregate)
Metrics Output
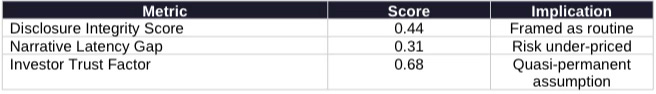
Interpretation
Market disclosures frame annual licenses as routine administrative compliance. Disclosure Integrity Score at 0.44 indicates selective revelation that minimizes perceived risk. Narrative Latency Gap at 0.31 shows markets lag structural reality. Investor Trust Factor at 0.68 indicates capital treats renewal as quasi-permanent unless explicit denial or new access controls materialize.
Market complacency creates a feedback loop: reduced political pressure for access-layer controls shortens the effective intervention window. Renewal risk remains under-priced, accelerating arbitrage of precarity.
Foresight Projection
CDT foresight simulation projects: By late 2026, capital markets will treat renewal as quasi-permanent unless explicit denial or new access controls are announced. Market complacency compounds the structural gap by reducing political pressure for access-layer controls before the Inevitability Threshold.
Capital markets are mispricing renewal risk. The mispricing reduces political urgency for the access-layer controls that would extend the intervention window.
VI. Exploit Pathway Probability Matrix
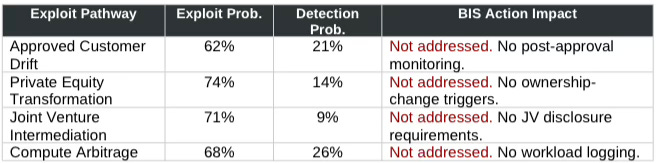
Prior MindCast AI publications identified four primary mechanisms through which capability flows to non-allied actors despite formal compliance with approval frameworks. The BIS action addressed none of these pathways. CDT foresight simulation validates that all four pathways remain operative under the new licensing regime. The matrix below quantifies exploit probability, detection probability, and BIS action impact for each pathway.
Assessment: Detection gaps persist across all four pathways. Exploit probability ranges from 60–74% while detection probability ranges from 9–26%. The BIS action did not narrow this gap. Causal Drop-Off Delta of −0.49 quantifies the structural failure.
All four exploit pathways remain operative. Annual licensing creates renewal leverage but does not address the capability-flow mechanisms that operate after chips leave the fab.
VII. Chicago School Law and Behavioral Economics Application
Regulatory effectiveness depends on whether controls change equilibrium behavior or merely add friction. Chicago School economic tests evaluate whether annual licensing alters the incentive structures that drive capability diffusion. CDT foresight simulation applies three foundational tests to the BIS action. Each test evaluates a distinct dimension of behavioral impact.
Vision Function Definition: The Chicago School Law and Behavioral Economics Composite Vision tests whether a regulatory system changes equilibrium behavior or merely adds friction. Components include the Coase Vision (transaction cost balance), the Becker Vision (incentive alignment), and the Posner Vision (efficient breach conditions).
Coase Test: Transaction Costs
Question: Do transaction costs for compliance exceed the costs of circumvention?
Result: FAILED. Transaction costs for laundering mature-node output through consolidated entities remain low. Annual licensing reduces administrative friction for legitimate operations without increasing friction for capability diffusion. Consolidated entities amortize compliance architecture across massive portfolios.
Becker Test: Incentive Alignment
Question: Do incentives align compliance behavior with policy intent?
Result: FAILED. State-backed entities optimize for national capability development, not export-control compliance. Expected penalty (low detection probability × uncertain sanctions) remains less than expected benefit (capability acquisition value).
Posner Test: Efficient Breach
Question: Does breach cost exceed capability acquisition value?
Result: FAILED. Breach cost (detection probability × sanction) remains substantially less than indigenous semiconductor development value. Efficient breach conditions persist.
Assessment: All three Chicago School tests fail on the same dimensions identified in prior MindCast AI H200 analysis. The BIS action did not alter the fundamental incentive structure that makes compliance theater rational and actual compliance irrational for state-coordinated actors.
VIII. Integrated Foresight Summary
Annual licensing creates leverage that decays over time. The following summary quantifies where renewal leverage still binds across the semiconductor stack and identifies the threshold beyond which intervention stops working. CDT foresight simulation integrates findings from Sections II–VII into conditional projections.
Key Findings
MindCast AI foresight simulations identify the following conditional conclusions:
Renewal leverage is front-loaded and decays faster than BIS can adapt (Institutional Update Velocity 0.41 versus consolidated entity adaptation)
China’s consolidated ecosystem reaches deterrent maturity by Q2 2027 (Coordination Coherence Coefficient 0.62, Strategic Convergence 0.71)—the Inevitability Threshold
Hardware-layer control without access-layer governance yields managed decline (Causal Drop-Off Delta −0.49)
Market complacency shortens effective intervention window (Investor Trust Factor 0.68, Narrative Latency Gap 0.31)
Timeline Projection
Final Foresight Simulation Prediction
MindCast AI foresight simulations predict:
Unless policymakers implement access-layer controls before the 2027 renewal cycle, annual licensing will no longer constrain China’s deployed artificial intelligence capability and will function only as administrative cost-shifting.
Foresight simulation produces this conclusion through causal modeling of institutional adaptation rates, consolidation dynamics, and capability-flow mechanisms. The prediction is simulation-derived, conditional, time-bound, and falsifiable.
IX. Falsification Conditions
The following conditions would falsify the foresight simulation and indicate that the BIS framework provides durable strategic protection. Rigorous foresight requires explicit falsification conditions stated before the fact.
Model Falsification Triggers
1. Significant slowdown in domestic tool substitution (greater than 12 months delay beyond current projections)
2. Implementation of workload identity logging or ownership recertification before Q1 2027
3. Observable market repricing of renewal risk (Investor Trust Factor declining below 0.50)
4. Detection probability improvement exceeding 35% across pathways by Q4 2027
5. Causal Drop-Off Delta reduction to below −0.25 through access-layer instrumentation
Absent these conditions, the projection stands.
Falsification conditions operationalize scientific rigor. The foresight simulation either survives empirical test or fails—and failure would indicate the BIS framework works better than the model predicts.
X. Conclusion
The BIS action represents meaningful progress on hardware-layer export controls. The action does not represent implementation of access-layer governance. The strategic gap between these two layers determines whether annual licensing constrains capability or merely shifts costs.
What the Bureau Action Represents
VEU revocation and annual licensing represent regulatory acknowledgment that the prior architecture was inadequate. BIS moved from permissive gate to restrictive gate with operational grandfathering. Input-Layer CSI at 0.61 confirms meaningful progress on hardware-layer export controls.
What the Bureau Action Does Not Represent
The action does not represent implementation of access-layer controls. Output-Layer CSI at 0.12 confirms that capability-flow pathways—drift, joint venture intermediation, ownership transformation, arbitrage—operate downstream of the licensing decision with minimal traceability. Causal Drop-Off Delta of −0.49 quantifies the structural gap between transaction-level compliance and capability-flow governance.
The Strategic Gap
The gate without the fence is now staffed by professionals. BIS hired guards for the gate (Input-Layer CSI 0.61). The fence remains unbuilt (Output-Layer CSI 0.12). The consolidated ecosystem on the other side has become more capable (Coordination Coherence Coefficient 0.62), more coordinated (Strategic Convergence 0.71), and more efficient (Capital Efficiency Ratio 0.59) at converting whatever passes through the gate into strategic capability.
MindCast AI foresight simulations identify Q2 2027 as the Inevitability Threshold—the point at which intervention stops working. Policymakers must implement access-layer controls before that threshold or accept that administrative continuity will be mistaken for strategic adequacy.
MindCast AI predicts inevitability thresholds, not events. The threshold is approaching.
All predictions in this publication are outputs of MindCast AI foresight simulations and are conditional on modeled incentives, constraints, and institutional adaptation rates.