MCAI Lex Vision: Institutional Chokepoints and Shadow Equilibria in Antitrust and Epstein Files
Cross-Domain Geometry of Federal Enforcement
Executive Summary
Federal enforcement in high-salience matters now clears through a monopsony of process operating inside a velocity gap between narrative markets and institutional throughput. The DOJ functions as the sole institutional buyer of enforcement and disclosure outcomes, converting political volatility into legal duration through procedural friction. Aligned incentives among institutional actors produce coordination-like delay without conspiracy—a pattern formalized here as Emergent Institutional Coordination (EIC). Three measurable variables—Credibility Discount Rate (CDR), Legitimacy Liquidity Risk (LLR), and Defense Suppression Coefficient (DSC)—quantify the conditions under which EIC activates and behavioral normalization prevails.
Two independent MindCast AI Cognitive Digital Twin (CDT) foresight simulation suites identified the monopsony-velocity structure across structurally distinct domains: criminal justice disclosure (Epstein Files) and antitrust enforcement (Shadow Antitrust Trifecta, DOJ Slater, Competitive Federalism, Assefi Test, Netflix–DOJ, Shadow Antitrust Credibility Threshold). The domains diverge at one structural variable: constraint node architecture. Antitrust enforcement possesses independent constraint nodes (state attorneys general, Tunney Act courts) that sustain scrutiny beyond congressional attention cycles. Epstein disclosure lacks equivalent nodes. Nine of ten antitrust predictions were confirmed. Forward falsification grids apply the model to three active windows: March antitrust trial and depositions, June Netflix-WBD decision, and mid-2026 Epstein disclosure horizon.
This paper is not commentary and not a normative manifesto. It is a cross-domain institutional foresight model with embedded falsification windows. The monopsony framework, the EIC diagnostic, and the CDR × LLR × DSC threshold together form a predictive geometry that can be tested in real time across active enforcement cycles. If the signals confirm, the model scales. If they fail, the architecture is revised.
I. Governing Structure: Narrative Velocity vs. Institutional Throughput
Institutional legitimacy erodes when narrative markets clear faster than evidentiary process. Courts require procedural sequencing, evidentiary standards, and adjudicative restraint. Narrative actors—media, political figures, social platforms, capital markets—operate without those constraints. When the gap widens, informal signaling substitutes for formal authority: markets price enforcement expectations before filings; political actors trade on belief volatility rather than disclosure outcomes; public attention cycles exhaust before procedural output materializes.
A. The Velocity Gap as Structural Precondition
Narrative markets clear in hours to days; institutional process clears in months to years
The gap creates an interpretive vacuum that informal actors fill—producing reputational volatility independent of evidentiary findings
Epstein: the 427–1 congressional vote (November 2025) generated peak narrative velocity while DOJ procedural output remained at baseline; the December 19 initial release drew bipartisan criticism for 500+ entirely blacked-out pages; the January 30 dump of 3.5 million pages claimed compliance while releasing only half the 6 million identified pages—each release widened rather than closed the velocity gap
Antitrust: AAG Slater’s February 12 departure generated immediate market response (LYV +4–5% intraday, extending to +14% over six trading days, approximately $1.5 billion in market cap appreciation) while DOJ enforcement posture remained procedurally unchanged
B. Shadow Equilibria
A shadow equilibrium forms when informal credibility signals materially influence institutional perception before formal adjudication concludes
Antitrust: Live Nation stock movement, reported unusual options activity around the HPE-Juniper settlement announcement, and Semafor’s characterization of the post-Slater environment constitute shadow pricing of enforcement outcomes
Epstein: Trump’s repositioning from resisting to championing release, Bondi’s February 2025 claim of having an Epstein “client list sitting on my desk” (later walked back by DOJ), and Blanche’s February 2 announcement of no further prosecutions each constitute shadow positioning—trading on belief volatility regardless of what the files contain
The interpretive vacuum operates in real time: on February 16, a 2018 USCIS naturalization ceremony notice found in the Epstein files generated immediate speculation about Epstein’s role in facilitating citizenship (@MarioNawfal, referencing file EFTA01683440)—a single document fragment producing narrative velocity that outpaces any institutional capacity to contextualize it
Desynchronization between narrative velocity and institutional throughput is a structural condition embedded in institutional design, not a communications failure. When narrative markets outpace procedural output, informal actors fill the resulting vacuum.
Contact mcai@mindcast-ai.com to partner with us on Law and Behavioral Economics foresight simulations. Companion publications: Shadow Antitrust Trifecta | DOJ Slater: Predicted Removal | Judicial Process as Competitive Federalism | The Assefi Test | Netflix–DOJ | Shadow Antitrust Credibility Threshold | Epstein Files | Geometry of Regulatory Capture | Competitive Federalism | Compass Astroturf Coefficient | Compass Narrative Inversion Playbook
II. The DOJ as Monopsony of Process
The Department of Justice monopolizes the procedural infrastructure through which enforcement and disclosure outcomes must pass. No merger settles and no sealed file is unsealed without transiting the same procedural gate. When a single buyer controls the exit, the buyer’s institutional incentives determine market-clearing conditions regardless of external demand signals.
A. The Monopsony Structure
DOJ as the sole buyer of enforcement outcomes (antitrust) and disclosure outcomes (Epstein)—no alternative institutional pathway exists absent independent constraint nodes
Congress, state legislatures, and media generate demand signals; only DOJ controls supply
Procedural friction functions as the institutional markup that converts political volatility into legal duration
B. Congressional Pressure as Risk Transfer
The 427–1 Epstein vote and the 12-letter antitrust oversight campaign perform identical structural functions: symbolic mandate transfer without operational commitment
Legislators extract reputational value at the moment of the vote or letter, then hand liability to DOJ
The Klobuchar-led seven-senator letter (February 15, 2026) named HPE-Juniper, Live Nation, and Compass as reported instances of staff being bypassed in a single document—yet operational authority remained with the same DOJ leadership the letter targeted
Epstein parallel: Representatives Khanna and Massie pressed for a Special Master (denied January 21); the House Judiciary Committee demanded immediate file access (January 31); Bondi testified at a heated oversight hearing (February 12) where she deflected substantive questions and was later photographed holding a printout of Rep. Jayapal’s search history—each escalation widened the symbolic-operational gap without altering DOJ’s procedural control
C. The Implicit Utility Function
DOJ optimizes across five variables in both domains: litigation/disclosure variance cost, political exposure cost, precedent control value, division autonomy value, and credibility discount rate. The DOJ optimizes not for maximum enforcement, but for variance-minimized clearance subject to political exposure constraints.
Under elevated scrutiny, CDR compounds—each behavioral settlement or redaction-heavy release reinforces the inference that the monopsony serves institutional interests rather than its mandate. Senator Blumenthal characterized Slater’s departure as “a chilling sign of the festering corruption & political interference at DOJ” (@SenBlumenthal, February 12, 2026)—language that prices CDR in the political market regardless of whether the characterization reflects structural friction or intentional obstruction
D. Procedural Friction as Duration Conversion
Antitrust mechanisms: eve-of-trial settlements, behavioral remedies preserving existing market structure, reported routing through Deputy AG’s office bypassing career staff recommendations
Epstein mechanisms: five statutory veto points (privacy rights, ongoing prosecutions, investigative sensitivity, risk to uninvolved individuals, law enforcement methodology) embedded in the Transparency Act by the same Congress that voted 427–1; DOJ’s January 30 release claimed full compliance despite producing only half the identified pages; approximately 200,000 pages were redacted or withheld citing attorney-client privilege, deliberative process privilege, and technical limitations
The institution that receives the mandate also controls the tools that convert urgency into duration
Increased external pressure produces diminishing returns because a sole buyer absorbs demand-side volatility through supply-side discretion. If policymakers seek structural outcomes, amplifying demand signals will not suffice; introducing alternative buyers through independent constraint nodes changes the clearing price.
III. Shared Geometries: Where the Domains Converge
Five independent structural parallels emerged from MindCast CDT analysis across the Epstein and antitrust suites without being designed to converge. Each operates through different statutory mechanisms but produces functionally identical outcomes.
Convergence Table
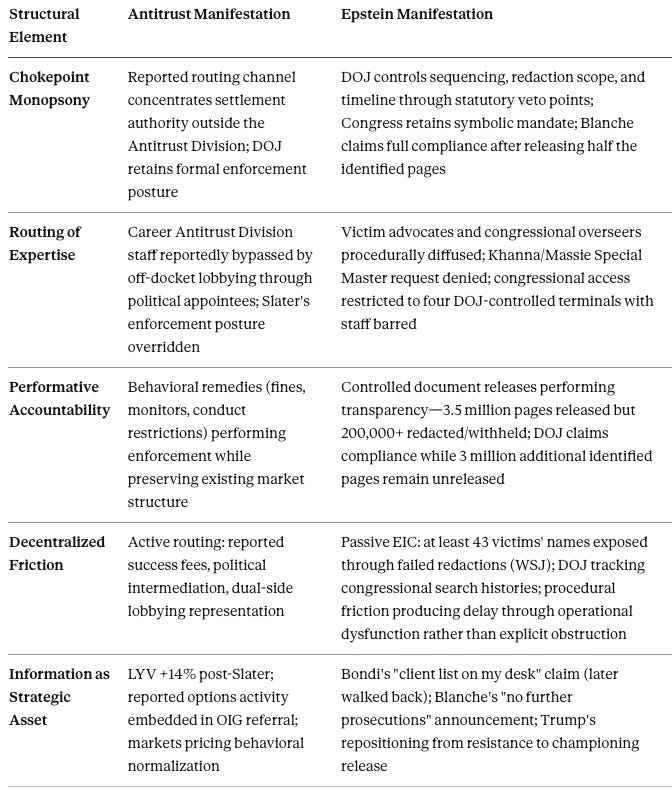
A. The Chokepoint Mechanism
Epstein: DOJ controls sequencing, redaction scope, and timeline through statutory veto points
Antitrust: reported routing channel concentrates settlement authority outside the Antitrust Division while DOJ retains formal posture
Shared geometry: formal authority concentrates in the institution least incentivized to exercise it aggressively
B. Behavioral Normalization as Equilibrium
Epstein: controlled document drips performing transparency while ensuring nothing destabilizes. Deputy AG Blanche articulated the mechanism directly: “We released over 3.5 million pieces of paper, which the entire world can look at now, and see if we got it wrong” (February 1, 2026 hearing, via @Acyn)—framing high-volume release as completion rather than the midpoint of a 6-million-page obligation
Antitrust: behavioral remedies performing enforcement while preserving existing market structure
Both domains calibrate institutional output to relieve pressure without altering structural conditions
C. Decentralized Self-Protection and Active Routing
Epstein (passive): elite actors filing protective orders, sealed motions, and privacy challenges—each motion adding weeks or months to review
Antitrust (active): reported success fees for merger clearance, political intermediaries meeting with DOJ officials, lobbying firms representing both sides of the same antitrust review
Passive and active capture occupy a single continuum; the antitrust context demonstrates observable deviation from standard process where the Epstein context demonstrates emergent delay
D. Scrutiny Density and Attention Economics
Epstein: congressional attention spikes at each release event (December 19, January 30, February 12 Bondi hearing) then decays between cycles because reputational value is extracted at each milestone (CDT projected the decay pattern in November 2025)
Antitrust: scrutiny density persists and compounds—12 congressional letters, 20 state AG objections, House Judiciary second front, Klobuchar’s February 15 letter naming three matters in a single document. On February 16, Senator Klobuchar posted: “Gail Slater—one of our top antitrust enforcers—was pushed out of the Justice Department just weeks prior to the Live Nation-Ticketmaster trial. This raises serious questions about the DOJ’s commitment to protecting consumers and small businesses” (@SenAmyKlobuchar, February 16, 2026)—the first senatorial statement publicly linking Slater’s departure to the trial timeline
The attention asymmetry is explained by the presence or absence of independent constraint nodes (Section IV)
Five structural parallels across two domains produce the same behavioral normalization outcome. The convergence validates portability. The divergence—Section IV—validates precision.
IV. Constraint Nodes: Why Antitrust Survives and Epstein Stalls
Antitrust enforcement possesses independent constraint nodes operating under separate legal authorities with autonomous incentives to sustain pressure. Epstein disclosure lacks equivalent nodes. Competitive federalism, formalized in Judicial Process as Competitive Federalism and Competitive Federalism and Significance of State Action, explains the divergence. Where constraint nodes exist, the monopsony faces price competition. Where they do not, it clears at its risk-minimization preference.
A. Antitrust Constraint Nodes
State attorneys general: 40-state Live Nation coalition can proceed without federal participation; Colorado AG Weiser’s Tunney Act intervention secured access to pretrial discovery; California AG Bonta’s February 12 assertion of independent enforcement authority
Tunney Act courts: Judge Pitts’s February 3 authorization of depositions (March 23–27)—the first moment where actors associated with the reported routing pattern face sworn testimony obligations to an authority outside it
Market discipline: capital markets price enforcement expectations in real time, creating a secondary observation layer outside DOJ procedural discretion
B. Epstein: The Absent Node
No state AG possesses independent statutory grounds to compel federal document release or conduct parallel investigation into disclosure process
Federal courts process individual redaction disputes but lack authority to interrogate the institutional process of withholding—Judge Engelmayer denied the Special Master request on January 21, preserving DOJ’s sole procedural control
Congressional access operates on DOJ-controlled infrastructure: four terminals, staff barred, search histories tracked—the oversight mechanism is itself administered by the entity being overseen
Congressional attention spikes at release events then decays because reputational extraction completes at each milestone
C. The Constraint Node Thesis as Generalizable Prediction
Falsifiable claim: if an independent constraint node emerges in the Epstein context (state AG investigation into related state-law violations, foreign jurisdiction disclosure, independent counsel appointment), the model predicts acceleration of substantive disclosure within 90 days
Absence of constraint nodes explains the multi-year arc projected in the original Epstein simulation
Competitive federalism functions as a structural variable, not a political preference
If policymakers seek structural outcomes in disclosure contexts, introducing independent enforcement pathways changes the clearing price of the monopsony
Constraint node architecture is the single strongest predictor of whether scrutiny converts into structural outcomes or dissipates. Antitrust enforcement survives congressional attention decay because state AGs and Tunney Act courts operate on independent institutional clocks. Epstein disclosure stalls because no equivalent pathway exists.
V. Emergent Institutional Coordination (EIC)
When multiple institutional actors share incentives to slow, redirect, or dilute enforcement or disclosure outcomes, their independent rational behaviors produce coordination-like effects without requiring conspiracy, communication, or even awareness of each other’s actions. The mechanism is Nash equilibrium among actors with aligned incentives operating within procedural systems that reward delay. Formalizing this as Emergent Institutional Coordination (EIC) provides a reusable diagnostic that distinguishes structural friction from intentional obstruction—and identifies the conditions under which the former transitions into the latter.
A. Formal Definition
EIC occurs when: (1) multiple actors face aligned incentives to slow or dilute an institutional outcome; (2) procedural mechanisms reward delay independently of strategic choice; (3) the resulting behavioral pattern is indistinguishable from coordinated action to an external observer; (4) no explicit coordination is required
The Epstein case is pure EIC: elite legal teams file protective orders, DOJ invokes statutory veto points, congressional actors extract reputational value—each actor optimizes independently; the aggregate effect is coordinated delay
The antitrust case demonstrates the EIC-to-active-capture transition: when intermediaries reportedly formalize the routing channel, the institutional environment that made active routing profitable was itself an EIC product
B. The Passive-Active Spectrum
Passive EIC (Epstein): aligned incentives producing emergent coordination through legitimate procedural tools
Active capture (Antitrust): intermediaries reportedly formalizing the routing channel through success fees, off-docket lobbying, and reported bypassing of career staff. Davis publicly confirmed the intermediation sequence across four February 13 posts: he “helped her land in the Trump 45 White House,” then “got her permission before accepting legal clients,” one of whom “appealed one of her decisions”—reframing off-docket lobbying through DOJ leadership as a routine legal appeal (@mrddmia, February 13, 2026, 629 likes). When the appeal succeeded and Slater resisted, Davis recharacterized her enforcement posture as personal failure: “She leaked, lied, disobeyed, and subverted. She got fired” (724 likes, 212 reposts). He then admitted: “I was the person who recommended Gail Slater for her job. It was a huge mistake” (244 likes)—completing the recommend → intermediate → recharacterize → remove arc that the Assefi Test identifies as the active capture transition signature. The victory lap—”I’m glad she’s gone” (489 likes)—confirms the intermediary treating personnel removal as a successful enforcement outcome
EIC predicts delay under aligned incentives; active capture predicts directional deviation from statutory baseline
The Assefi Test provides the leadership-sorting diagnostic that identifies the transition point
EIC is the baseline expectation for any federal institution under political pressure; active capture is the deviation requiring additional evidence
C. EIC vs. Conspiracy
Conspiracy requires coordination and shared intent; EIC requires only aligned incentives within procedural systems that reward delay
Reform prescription follows: conspiracy demands investigation; EIC demands structural redesign and alternative enforcement pathways
The public perception gap is observable: commentator Robert Barnes described Bondi as “perverting justice by interfering w/ the AntiTrust division at the DOJ” (@barnes_law, February 7, 2026, 629 likes, 262 reposts)—language framing structural outputs as intentional corruption. The EIC framework explains why the public perceives conspiracy where aligned incentives within procedural systems produce identical observable outputs without requiring coordination
D. Cross-Domain Application Map
Healthcare enforcement: FDA approval processes under pharmaceutical lobbying pressure
Financial regulation: SEC enforcement under revolving-door personnel dynamics
Export controls: Commerce Department BIS licensing under competing national security and commercial incentives
Legislative advocacy: state-level regulatory capture through astroturfing (documented in the Compass Astroturf Coefficient)
EIC connects the Epstein and antitrust analyses at the level of mechanism rather than analogy. Any federal enforcement or disclosure domain exhibiting the four EIC conditions can be assessed for behavioral normalization risk before outcomes materialize.
VI. Measuring the Architecture: CDR, LLR, and DSC
Structural comparison without measurable variables remains descriptive. Three variables quantify the institutional environment that determines whether EIC produces behavioral normalization or constraint nodes force structural outcomes.
A. Credibility Discount Rate (CDR)
Definition: the reputational cost imposed when enforcement or disclosure outcomes fall below the stated institutional mandate, discounted by the intensity of public scrutiny at the time of the outcome
Directionality: ↑ CDR → ↑ probability of behavioral normalization in subsequent matters. CDR compounds sequentially—behavioral normalization in one matter reduces the political cost of behavioral normalization in the next
Observable proxies: gap between stated enforcement theory and settlement/disclosure terms; sequential compounding across multiple matters (reported behavioral normalization in HPE-Juniper → Compass clearance → Live Nation settlement posture compounds CDR faster than any single matter); market pricing of enforcement expectations (LYV post-Slater rally prices CDR in real time)
B. Legitimacy Liquidity Risk (LLR)
Definition: the rate at which institutional trust converts into reputational volatility under conditions of incomplete information
Directionality: ↑ LLR → ↑ speed of shadow equilibrium formation. Higher LLR means informal actors fill the interpretive vacuum faster, producing reputational volatility before institutional output materializes
Observable proxies: time lag between demand signal and substantive institutional output; information gap width (ratio of public questions to authoritative answers); narrative actor fill rate (volume of informal interpretation per unit of institutional silence)
Cross-domain asymmetry: LLR is structurally higher in criminal justice contexts—moral finality amplifies trust-to-volatility conversion at roughly 2–3× the rate observed in regulatory contexts, where market signals permit incremental measurement and dampen narrative fill rates
C. Defense Suppression Coefficient (DSC)
Definition: the reputational penalty associated with defending institutional process relative to attacking it
Directionality: ↑ DSC → ↑ institutional silence under scrutiny. When DSC is maximal, no political actor can defend process without incurring reputational damage, eliminating the institutional counter-narrative and accelerating LLR
Observable proxies: ratio of actors publicly defending institutional process vs. demanding action; political positioning data around key enforcement events; the 427–1 Epstein vote as maximal DSC (even actors who benefit from delay must publicly support disclosure). Davis’s February 13–15 posts quantify the DSC mechanism in real time: he dismissed Epstein file scrutiny as “this Epstein bullshit” (@mrddmia, February 13, 2026, 4,082 likes), labeled Representatives Massie and Khanna “shameful demagogue politicians” whose oversight is “Exhibit A why you don’t publicly release unverified investigatory files” (1,726 likes, 479 reposts), characterized the entire disclosure push as Massie “fundraising off of his latest Epstein hoax” (4,516 likes, 1,374 reposts), and called Massie’s ABC appearance a “useful liberal media darling” act (3,926 likes, 852 reposts). Each post raises the reputational cost of oversight while generating no substantive defense of the redaction decisions—pure defense suppression through attack rather than argument
Cross-domain asymmetry: DSC is maximal in the Epstein context (defending redactions is politically impossible) and high but submaximal in antitrust (industry actors can frame behavioral settlements as pragmatic enforcement)
D. The CDR × LLR × DSC Threshold
Interaction logic: multiplicative, not additive. Elevated CDR reduces the political cost of future normalization; elevated LLR accelerates shadow equilibrium formation; elevated DSC eliminates institutional defense. Simultaneous elevation meets EIC activation conditions
Threshold formulation:
P(Behavioral Normalization) ∝ CDR × LLR × DSC / Constraint Node Strength
Prediction: any federal enforcement or disclosure domain where CDR, LLR, and DSC simultaneously exceed threshold values will produce behavioral normalization within 180 days of initial symbolic action, absent independent constraint nodes
Constraint node modifier: independent nodes increase the denominator, forcing clearing closer to mandate even under elevated numerator conditions
CDR, LLR, and DSC transform structural analogy into measurable institutional engineering. Their multiplicative interaction produces a threshold model that predicts behavioral normalization before outcomes materialize.
VII. CDT Methodological Evolution: From Proof-of-Concept to Institutional Engineering
The Epstein Files analysis (November 2025) and the Shadow Antitrust suite (January–February 2026) represent two stages of CDT development: institutional logic modeling → falsifiable prediction → institutional engineering.
A. The Epstein Suite as Proof-of-Concept
Four CDTs (Congressional, DOJ, Narrative-Executive, Elite-Legal) modeling institutional behavior under uncertainty
Predictive timeline: 8-week arc projections, mid-2026 disclosure window
Core thesis established: “the entity controlling pace controls outcomes”
Limitation: predictive but not yet formally falsifiable—no binary observables, no named variables, no symmetric falsification conditions
Validation update (February 2026): the January 30 document dump, Blanche’s “no further prosecutions” announcement (February 2), and DOJ’s claimed compliance despite releasing only half the identified pages track the CDT’s projected arc—controlled drips performing transparency while ensuring nothing destabilizes; congressional attention spiking and decaying at each milestone
B. The Antitrust Suite as Formalization
Named metrics: Scrutiny Density, Credibility Discount Rate, Behavioral Normalization, Grammar Persistence Index, Update Elasticity, Astroturf Coefficient
30/90/180-day falsification grid with binary observables and symmetric update rules
Nine of ten falsifiable predictions confirmed before or upon Slater’s departure
Cross-forum synthesis (Compass across federal court, state legislature, and consumer marketing) as methodological proof of multi-forum analysis
C. The Cross-Domain Synthesis as Institutional Engineering
CDR, LLR, and DSC complete the measurable toolkit—environment variables predicting EIC activation
EIC provides the named principle—reusable diagnostic transforming case-specific analysis into generalizable institutional science
The Constraint Node Gap provides the prescriptive element—competitive federalism as structural variable
The maturation arc is itself a falsifiable claim. If the cross-domain variables fail to predict outcomes in the next enforcement cycle, the thesis weakens. The next 180 days provide the test.
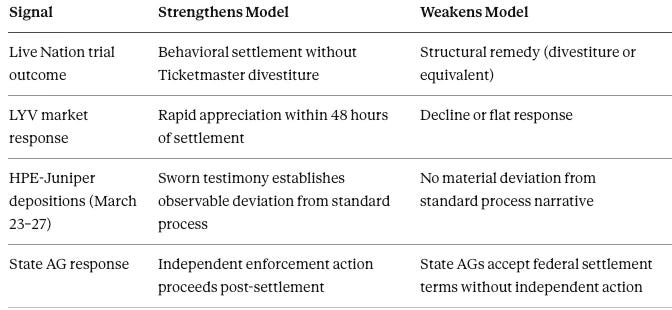
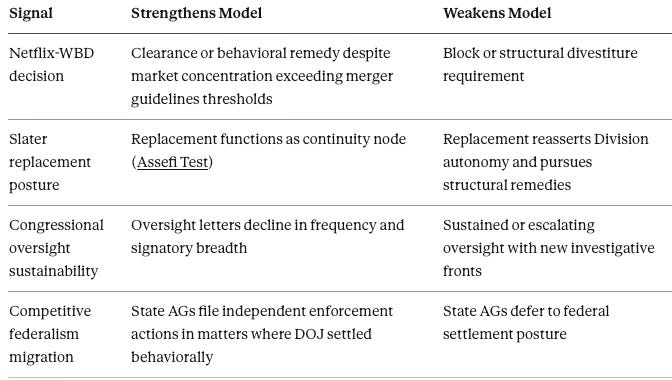
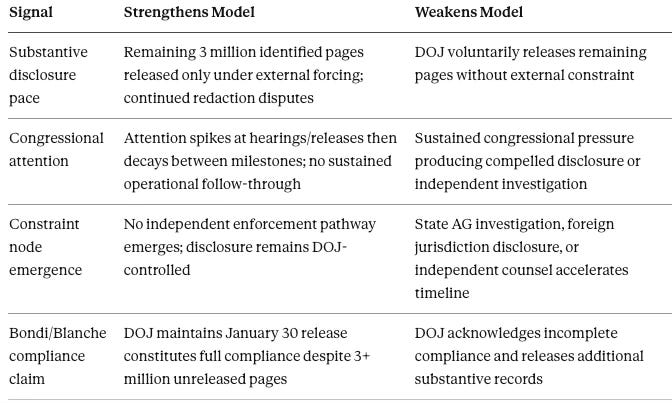
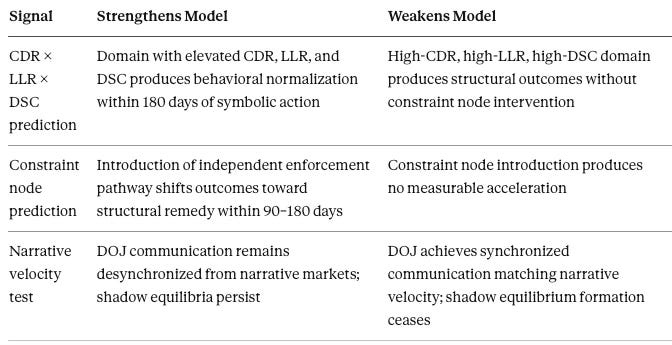
VIII. Falsification Grid: 30 / 90 / 180-Day Observable Signals
Forward predictions without falsification conditions are advocacy. Each signal below is binary or near-binary. Symmetric conditions specify what strengthens and what weakens the model with equal precision.
⚡ Live Test: March 23–27 Tunney Act Depositions
Mike Davis (Article III Project founder, reported $1M+ in success fees for both HPE-Juniper clearance and Compass-Anywhere clearance—deploying the same reported routing mechanism through Blanche's office on both matters), Brad Schwartz (HPE outside counsel), and Daniel Levi (former Duke Law dean, HPE board member) face sworn testimony before Judge Pitts on the reported off-docket routing channel. Admissions of intermediation strengthen the EIC-to-active-capture transition claim and compound CDR across the antitrust docket. Standard-process testimony weakens the routing geometry thesis and returns the model to the null hypothesis of ordinary bureaucratic variance.
A. Antitrust Window (30 Days: March 2–27, 2026)
B. Antitrust Window (90 Days: Through June 2026)
C. Epstein Disclosure Window (180 Days: Through August 2026)
D. Cross-Domain Threshold (180 Days)
E. High-Stakes Falsifier
If Live Nation produces structural divestiture under high-CDR, high-LLR, and high-DSC conditions without independent constraint node pressure forcing the outcome, the cross-domain geometry thesis materially weakens. The monopsony framework, the EIC activation model, and the CDR × LLR × DSC threshold would each require fundamental recalibration. MindCast commits to publishing a full methodological revision with equal specificity.
Eighteen binary signals across four windows and one high-stakes falsifier. If a majority of 30-day signals confirm, the model holds for 90-day application. If a majority weaken the model in any window, the revision publishes with equivalent precision.
IX. Conclusion: Two Domains, One Geometry
Geometry drives institutional behavior, not intent. The same monopsony mechanism, the same EIC pattern, and the same constraint node divergence appear across criminal justice disclosure and antitrust enforcement. The underlying institutional logic engine produces consistent structural signatures regardless of subject matter.
If policymakers seek structural enforcement outcomes, amplifying demand signals will not suffice. Introducing alternative enforcement nodes—through competitive federalism, judicial discovery authority, or independent institutional pathways—changes the clearing price of the monopsony. Three active enforcement windows test the architecture within 180 days. Updates will publish with the same symmetric falsifiability as the original predictions.
The pattern scales. The question is whether we do.