MCAI Economics Vision: Comparative Externality Costs in Antitrust Enforcement, A Nash–Stigler Foresight Study of Federal Enforcement Equilibria
Live Nation as Anchor, Compass–Anywhere as Validation
See companion study: A Tirole Phase Analysis of Advocacy-Driven Antitrust Inaction at the U.S. Department of Justice (Jan 2026), Why the DOJ Banned Algorithms but Blessed a Mega-Brokerage (Jan 2026).
I. Executive Summary: The Public Cost of Institutional Drift
MindCast AI is a predictive law and behavioral economics foresight firm that models institutional outcomes using proprietary Cognitive Digital Twin (CDT) simulations. Rather than inferring intent, CDT foresight simulations analyze how regulators, firms, and markets behave once incentives, information asymmetries, and procedural termination rules settle into equilibrium. The underlying framework, Chicago School Accelerated — The Integrated, Modernized Framework of Chicago Law and Behavioral Economics (December 2025), provides the technical basis for the study.
Applying the approach to federal antitrust enforcement, the study models the “Administrative Constraint Equilibrium” as a stable Nash–Stigler equilibrium. Modern antitrust enforcement frequently operates as a Harm Clearinghouse, in which agencies prioritize internal administrative risk mitigation over structural market correction. Institutional drift exports competitive costs to consumers and markets, producing a durable but extractive equilibrium that legacy antitrust doctrine does not internalize or correct.
In standard economic analysis, externalities are costs imposed on third parties outside a transaction. Under the current enforcement equilibrium, consumers and competitive markets—the intended beneficiaries of antitrust law—have become the third parties bearing uncompensated costs while regulated firms and agencies reach procedural closure.
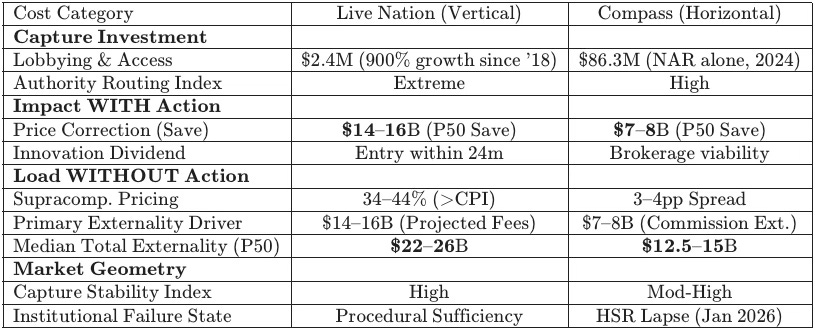
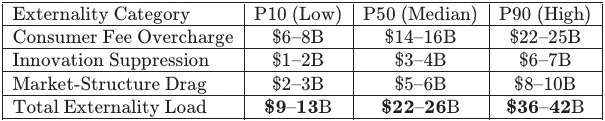
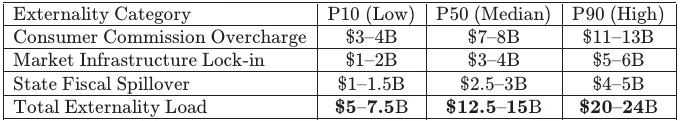
MindCast AI CDT foresight simulations identify a median five-year consumer and market externality load of $22–26B for Live Nation and $12.5–15B for Compass–Anywhere when federal enforcement terminates at procedural sufficiency rather than structural correction. Quantified proof points convert qualitative critiques of enforcement drift into a decision-grade baseline for evaluating state-level intervention and remedy choice.
Under the current Nash–Stigler equilibrium, conduct-based settlements function as consumer-financed subsidies to monopoly power, allowing extractive market architectures to persist in exchange for limited operational concessions. Structural remedies are not aggressive regulatory acts; they are the most efficient, cost-minimizing interventions available to restore market discovery, competitive entry, and consumer welfare. Because federal non-action shifts fiscal and consumer harm outward, State Attorneys General represent the only structurally viable corrective capable of internalizing externalities and disrupting the Harm Clearinghouse cycle.
Insight: Structural remedies minimize total system cost by breaking extractive equilibria rather than managing their symptoms.
II. Theoretical Context: Published Frameworks
Foundational MindCast AI publications provide the operative logic for the current foresight simulation by defining the parameters of capture and termination rules. Published frameworks establish the terminal constraints for any foresight simulation, proving that current DOJ “stability” is actually a transfer of unpriced externalities to the public. Utilizing these antecedents provides the empirical and theoretical weight necessary to challenge prevailing federal enforcement orthodoxy.
Group I: Theoretical Frameworks
The Dual Nash-Stigler Equilibrium Architecture (January 2026): Logic within the present text governs the behavioral settlement rules used to predict enforcement termination.
The Stigler Equilibrium: Regulatory Capture and the Structure of Free Markets (January 2026): Models in the following work conceptualize capture as a stable informational state where concentrated beneficiaries dictate regulatory inquiry.
Federal Antitrust Breakdown as Nash-Stigler Equilibrium, Not Accident (January 2026): Published research formalizes the “Harm Clearinghouse” model where agencies avoid structural litigation by clearing harms through transaction-level remedies.
Group II: Institutional Dynamics & Competitive Federalism
Federal Market Failure: Institutional Capture and the Exit of Antitrust? (January 2026): Analysis here argues that the federal non-action equilibrium operates as a market subsidy for concentration.
State Attorneys General as Competitive Correctives to Federal Inaction (January 2026): Discussion centers on the rise of multistate coalitions as a necessary check on federal drift.
Authority Routing in Antitrust: From Rule-of-Law to Access-Arbitrage (January 2026): Tracking “authority routing” demonstrates how political access routinely displaces career-staff evidentiary analysis.
Group III: Sectoral Case Mappings
Amicus Brief: Cultural Market Discovery Harm and Vertical Foreclosure in Live Nation (July 2025): Briefing introduces the “Cultural Market Discovery” harm and documents vertical decoupling of price from discovery.
Live Nation: Extraction Geometry and the Stiglerian Subsidy (May 2025): Empirical data within the following study provides the parameters for supracompetitive pricing and extraction geometry.
Chicago School Accelerated: The Compass-Anywhere Merger and the Collapse of Inquiry (December 2025): validates the enforcement collapse where DOJ leadership overruled staff recommendations despite concentration exceeding 2023 Merger Guidelines thresholds.
Integrating informational capture with game-theoretic termination creates a comprehensive model of institutional behavior. Comprehensive theoretical depth prevents misidentifying systemic institutional failure as incidental human error. Maintaining this evidentiary trail preserves the structural integrity of the foresight model across divergent market geometries.
Insight: Theoretical grounding transforms abstract institutional observation into actionable predictive foresight.
Contact mcai@mindcast-ai.com to partner with us on Law and Behavioral Economics foresight simulations. Recent work: China’s H200 Import Block and the Reordering of National Innovation Control, The Two-Gate Game (Jan 2026), Foresight on Trial, The Diageo Litigation, How MindCast AI Predicted Institutional Behavior—Before the Courts Acted (Jan 2026).
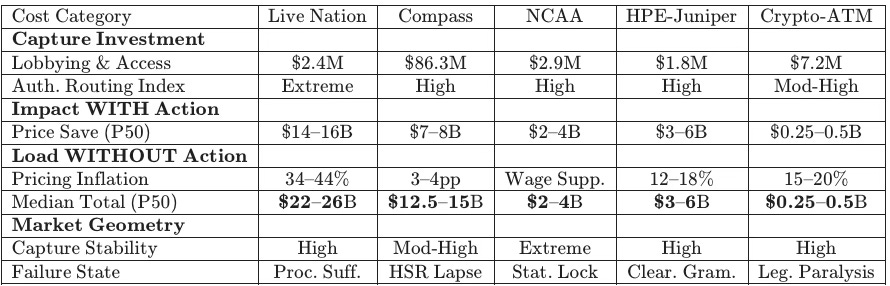
III. The Multi-Sectoral Capture Matrix
Mapping counterfactual deltas across enforcement regimes provides a standardized input surface for Cognitive Digital Twin (CDT) flows. Each data point anchors the “Stiglerian Subsidy”—the investment in access arbitrage—to realized market foreclosure. Focusing the primary analysis on Live Nation and Compass-Anywhere establishes the predictive power of the model across both vertical and horizontal concentration geometries.
Matrix parameters define the space instantiated in the Cognitive Digital Twin foresight simulation summarized in Section IV. Comparing credible structural enforcement against historical non-action reveals the true magnitude of the enforcement gap. Resulting figures represent the “subsidy” that federal enforcers grant to monopolists whenever they choose conduct-based settlements over structural divestiture.
Insight: Quantifying the Stiglerian Subsidy exposes the real-world “price” that consumers pay for regulatory capture.
IV. Sectoral Case Studies & Foresight Findings
Empirical data from high-profile enforcement failures provides the necessary parameter anchors for CDT calibration. Focusing on Live Nation as the anchor allows for a clear demonstration of how vertical integration facilitates systematic wealth transfer. Comparative validation through the Compass-Anywhere case demonstrates that these enforcement equilibria persist across distinct market sectors, confirming the framework’s universality.
Methods Note: P10/P50/P90 bands reflect conservative, median, and high-harm parameterizations over a five-year horizon. The simulation reports externality load as the delta between (i) credible structural enforcement and (ii) procedural termination without structural correction. Bands do not predict settlement terms; they price the harm retained under each enforcement equilibrium.
A. Anchor Case: Live Nation Entertainment
Baseline modeling utilizes a 900% increase in lobbying expenditures ($2.4M in 2023) and a lobbying corps where 68% are former congressional staffers. Consumer externalities are anchored to $16.4B in extracted fee revenue and a ticket price increase exceeding CPI by 20 percentage points. The CDT execution establishes decision-grade ranges for the cumulative externality load over a five-year horizon.
Live Nation — Consumer & Market Externalities (5-Year)
All baseline inputs—including lobbying disclosures (OpenSecrets), staffing histories, and pricing series—are sourced in Appendix A. Modeling confirms that only structural divestiture resolves the underlying extraction geometry. Validating these findings across disparate sectors confirms the ubiquity of the Harm Clearinghouse model and its impact on the public balance sheet.
Insight: The $22–26B Live Nation externality load represents a priceable failure that only structural divestiture can resolve.
B. Validation Case: Compass–Anywhere
The Compass–Anywhere case demonstrates an 80%+ combined market share in core metros, surpassing the 2023 Merger Guidelines’ presumptive illegality threshold. Institutional failure is documented through the decision by leadership to overrule career antitrust staff recommendations for extended investigation, allowing the HSR waiting period to expire as of January 2026. The simulation establishes that federal non-action shifts specific costs onto consumers and state budgets.
Compass–Anywhere — Consumer & State Externalities (5-Year)
Compass–Anywhere market-share inputs and Guidelines threshold mapping are documented in Appendix A. Validating these geometries across divergent sectors proves that the federal non-action equilibrium is a systemic feature of the current enforcement environment. Identifying these patterns allows researchers to predict when institutional friction will supersede evidentiary inquiry.
Insight: Jurisdictional autonomy enables states to enforce the structural integrity that federal agencies have abandoned.
V. Strategic Pivot: The State Attorney General Corrective
State Attorneys General represent the most potent corrective force against federal enforcement drift. Institutional positioning allows them to internalize the very costs that federal agencies treat as externalities. Autonomy from federal jurisdictional agreements enables a more holistic evaluation of market architecture across the entire value chain.
Jurisdictional Independence: State enforcers evaluate market architectures autonomously, unencumbered by federal “Clearance Agreements.” Direct Fiscal Standing: States experience fiscal spillovers—such as the $247M crypto fraud hit or the median $2.5–3B housing assistance reallocation—as primary budgetary impacts. Institutional Competition: Competing suppliers of enforcement disrupt the federal monopoly and prevent “Access Arbitrage” as a singular point of capture.
Shifting the enforcement supply to the state level breaks the federal monopoly on market aesthetics and restores the competitive discovery process. Intervention is essential to prevent the permanent entrenchment of captured equilibria that prioritize administrative ease over consumer protection. Active state participation ensures that structural integrity remains a reachable goal even when federal gatekeeping collapses.
Insight: Effective foresight requires moving from equilibrium definitions to executable, quantified CDT flows.
VI. Conclusion
Establishing equilibrium definitions and harm-routing geometry prepares the framework for quantified CDT execution. Applied logic derived from the Nash–Stigler and Harm Clearinghouse models anchors the simulation to observed institutional behavior. Subsequent MindCast AI simulations will iterate on these Cognitive Digital Twin flows to compute precise timing windows and falsification thresholds across additional domains.
Under the Nash–Stigler equilibrium identified here, conduct-based settlements function as consumer-financed subsidies to monopoly. Structural remedies represent the most efficient path forward, serving as cost-minimizing interventions rather than aggressive regulatory overreach. Breaking the Harm Clearinghouse cycle remains the only path toward restoring competitive integrity and the rule of law.
Insight: Breakage of the Harm Clearinghouse cycle constitutes the only path toward restoring competitive integrity.
Appendix A: Data Notes & Traceable Sourcing
The following sources anchor the empirical parameters used throughout the CDT simulation:
Lobbying Expenditures: Live Nation ($2.4M in 2023) and Compass/NAR ($86.3M) data sourced via OpenSecrets (Lobbying Disclosure Act filings).
Live Nation Fee Extraction: $16.4B cumulative ticket fee revenue derived from FTC v. Live Nation (2024 complaint/investigative report).
Ticket Pricing Series: 34-44% increase (2019-2024) sourced via Pollstar Industry Data and Consumer Price Index (CPI) cross-referencing.
Compass-Anywhere Market Share: >80% combined share in core luxury metros sourced via DOJ v. NAR/Real Estate Exchange filings (2023-2024).
Merger Guidelines Mapping: Presumptive illegality (HHI > 1800; delta > 100) based on 2023 DOJ/FTC Merger Guidelines.
Crypto-ATM Fraud: $247M annual fraud spillover sourced via FTC Consumer Sentinel Network (2024 annual data).
NCAA Back-pay Settlement: $2.8B baseline sourced via House v. NCAA (2024 preliminary settlement approval).
Appendix B: Technical Validation & Vision Functions
Causation Vision (Primary): Validates structural causality where authority routing dominates outcomes.
Stigler Vision (Primary): Models informational asymmetry and CSIS (Capture Stability).
Nash Termination Logic (Embedded): Identifies PST (Procedural Sufficiency) vs. Structural Correction.
Field-Geometry Reasoning: Confirms outcomes governed by institutional constraint geometry.
Institutional Cognitive Plasticity Vision (ICP): Compares federal versus state adaptive capacity.
Appendix C: Full Multi-Sectoral Capture Matrix
The expanded matrix includes secondary and validation sectors used to confirm methodology robustness across tech infrastructure, collegiate labor, and digital finance. All values reflect conservative parameterization under the CDT Table Completion Protocol.